Colorectal Polyp Image Detection and Classification through Grayscale Images and Deep Learning
- PMID: 34577209
- PMCID: PMC8470682
- DOI: 10.3390/s21185995
Colorectal Polyp Image Detection and Classification through Grayscale Images and Deep Learning
Abstract
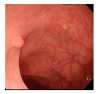
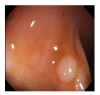
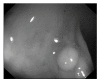
Colonoscopy screening and colonoscopic polypectomy can decrease the incidence and mortality rate of colorectal cancer (CRC). The adenoma detection rate and accuracy of diagnosis of colorectal polyp which vary in different experienced endoscopists have impact on the colonoscopy protection effect of CRC. The work proposed a colorectal polyp image detection and classification system through grayscale images and deep learning. The system collected the data of CVC-Clinic and 1000 colorectal polyp images of Linkou Chang Gung Medical Hospital. The red-green-blue (RGB) images were transformed to 0 to 255 grayscale images. Polyp detection and classification were performed by convolutional neural network (CNN) model. Data for polyp detection was divided into five groups and tested by 5-fold validation. The accuracy of polyp detection was 95.1% for grayscale images which is higher than 94.1% for RGB and narrow-band images. The diagnostic accuracy, precision and recall rates were 82.8%, 82.5% and 95.2% for narrow-band images, respectively. The experimental results show that grayscale images achieve an equivalent or even higher accuracy of polyp detection than RGB images for lightweight computation. It is also found that the accuracy of polyp detection and classification is dramatically decrease when the size of polyp images small than 1600 pixels. It is recommended that clinicians could adjust the distance between the lens and polyps appropriately to enhance the system performance when conducting computer-assisted colorectal polyp analysis.
Keywords: colonoscopy; colorectal polyp; computer-assisted colorectal polyp analysis; convolutional neural network; grayscale image.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






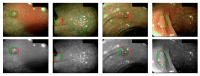
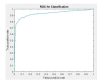
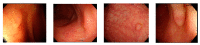

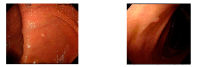


Similar articles
-
Improved Accuracy in Optical Diagnosis of Colorectal Polyps Using Convolutional Neural Networks with Visual Explanations.Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun;158(8):2169-2179.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.036. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 32119927
-
Detection and Classification of Colorectal Polyp Using Deep Learning.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 15;2022:2805607. doi: 10.1155/2022/2805607. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9879585. doi: 10.1155/2024/9879585. PMID: 35463989 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Deep Learning Localizes and Identifies Polyps in Real Time With 96% Accuracy in Screening Colonoscopy.Gastroenterology. 2018 Oct;155(4):1069-1078.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.037. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29928897 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges Facing the Detection of Colonic Polyps: What Can Deep Learning Do?Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Aug 12;55(8):473. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080473. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31409050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning to find colorectal polyps in colonoscopy: A systematic literature review.Artif Intell Med. 2020 Aug;108:101923. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101923. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Artif Intell Med. 2020. PMID: 32972656
Cited by
-
Intraprocedure Artificial Intelligence Alert System for Colonoscopy Examination.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;23(3):1211. doi: 10.3390/s23031211. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772251 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing adaptive deformable convolution and position embedding for colon polyp segmentation with a visual transformer.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57993-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538774 Free PMC article.
-
The role of deep learning in diagnosing colorectal cancer.Prz Gastroenterol. 2023;18(3):266-273. doi: 10.5114/pg.2023.129494. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Prz Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37937113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-Powered Object Detection in Radiology: Current Models, Challenges, and Future Direction.J Imaging. 2025 Apr 30;11(5):141. doi: 10.3390/jimaging11050141. J Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40422999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early prediction of colorectal adenoma risk: leveraging large-language model for clinical electronic medical record data.Front Oncol. 2025 May 15;15:1508455. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1508455. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40444092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki H., Yamamura T., Nakamura M., Hsu C.M., Su M.Y., Chen T.H., Chiu C.T., Hirooka Y., Goto H. An International Study on the Diagnostic Accuracy of the Japan Narrow-Band Imaging Expert Team Classification for Colorectal Polyps Ob-served with Blue Laser Imaging. Digestion. 2020;101:339–346. doi: 10.1159/000499856. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

