A Comprehensive Review of Techniques for Processing and Analyzing Fetal Heart Rate Signals
- PMID: 34577342
- PMCID: PMC8469481
- DOI: 10.3390/s21186136
A Comprehensive Review of Techniques for Processing and Analyzing Fetal Heart Rate Signals
Abstract
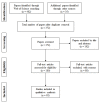
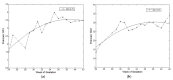
The availability of standardized guidelines regarding the use of electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) in clinical practice has not effectively helped to solve the main drawbacks of fetal heart rate (FHR) surveillance methodology, which still presents inter- and intra-observer variability as well as uncertainty in the classification of unreassuring or risky FHR recordings. Given the clinical relevance of the interpretation of FHR traces as well as the role of FHR as a marker of fetal wellbeing autonomous nervous system development, many different approaches for computerized processing and analysis of FHR patterns have been proposed in the literature. The objective of this review is to describe the techniques, methodologies, and algorithms proposed in this field so far, reporting their main achievements and discussing the value they brought to the scientific and clinical community. The review explores the following two main approaches to the processing and analysis of FHR signals: traditional (or linear) methodologies, namely, time and frequency domain analysis, and less conventional (or nonlinear) techniques. In this scenario, the emerging role and the opportunities offered by Artificial Intelligence tools, representing the future direction of EFM, are also discussed with a specific focus on the use of Artificial Neural Networks, whose application to the analysis of accelerations in FHR signals is also examined in a case study conducted by the authors.
Keywords: artificial neural networks; biomedical signal processing and analysis; fetal heart rate; fetal heart rate variability; linear FHRV indices; nonlinear FHRV indices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdulhay E.W., Oweis R.J., Alhaddad A.M., Sublaban F.N., Radwan M.A., Almasaeed H.M. Review Article: Non-Invasive Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Techniques. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2014;2:53–67. doi: 10.12691/bse-2-3-2. - DOI
-
- Stylios C. IFMBE Proceedings. Volume 11. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2005. Methods and Tools for Processing Biosignals: A Survey Paper; pp. 1727–1983.
-
- Lobo Marques J.A., Cortez P.C., Madeiro J.P.D.V., Fong S.J., Schlindwein F.S., Albuquerque V.H.C.D. Automatic Cardiotocography Diagnostic System Based on Hilbert Transform and Adaptive Threshold Technique. IEEE Access. 2019;7:73085–73094. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877933. - DOI
-
- Cesarelli M., Romano M., Bifulco P., Improta G., D’Addio G. An Application of Symbolic Dynamics for FHRV Assessment. Volume 180. IOS Press; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

