Particle Classification through the Analysis of the Forward Scattered Signal in Optical Tweezers
- PMID: 34577401
- PMCID: PMC8470432
- DOI: 10.3390/s21186181
Particle Classification through the Analysis of the Forward Scattered Signal in Optical Tweezers
Abstract
The ability to select, isolate, and manipulate micron-sized particles or small clusters has made optical tweezers one of the emergent tools for modern biotechnology. In conventional setups, the classification of the trapped specimen is usually achieved through the acquired image, the scattered signal, or additional information such as Raman spectroscopy. In this work, we propose a solution that uses the temporal data signal from the scattering process of the trapping laser, acquired with a quadrant photodetector. Our methodology rests on a pre-processing strategy that combines Fourier transform and principal component analysis to reduce the dimension of the data and perform relevant feature extraction. Testing a wide range of standard machine learning algorithms, it is shown that this methodology allows achieving accuracy performances around 90%, validating the concept of using the temporal dynamics of the scattering signal for the classification task. Achieved with 500 millisecond signals and leveraging on methods of low computational footprint, the results presented pave the way for the deployment of alternative and faster classification methodologies in optical trapping technologies.
Keywords: Brownian motion; optical trapping; optical tweezers; particle identification; principal component analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
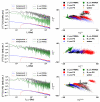
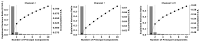



Similar articles
-
Enhancing Raman tweezers by phase-sensitive detection.Anal Chem. 2007 May 15;79(10):3708-15. doi: 10.1021/ac070050n. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Anal Chem. 2007. PMID: 17444615
-
Raman Spectroscopy of Optically Trapped Single Biological Micro-Particles.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Aug 4;15(8):19021-46. doi: 10.3390/s150819021. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26247952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laser Tweezers Raman Microspectroscopy of Single Cells and Biological Particles.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1745:219-257. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7680-5_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29476472
-
Superresolution imaging in optical tweezers using high-speed cameras.Opt Express. 2010 Feb 15;18(4):3322-31. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.003322. Opt Express. 2010. PMID: 20389339
-
Probing the micro-rheological properties of aerosol particles using optical tweezers.Rep Prog Phys. 2014 Jul;77(7):074601. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/77/7/074601. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2014. PMID: 24994710 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning for optical tweezers.Nanophotonics. 2024 May 23;13(17):3017-3035. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2024-0013. eCollection 2024 Jul. Nanophotonics. 2024. PMID: 39634937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward Nano- and Microplastic Sensors: Identification of Nano- and Microplastic Particles via Artificial Intelligence Combined with a Plasmonic Probe Functionalized with an Estrogen Receptor.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 18;9(17):18984-18994. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09485. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38708270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai Y., Alali H., Pan Y., Videen G., Wang C. Single-particle optical-trapping Raman spectroscopy for the detection and identification of aerosolized airborne biological particles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021;32:055207. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/abd5f1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

