Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition for Decoding Perception of Faces Using Magnetoencephalography
- PMID: 34577441
- PMCID: PMC8472346
- DOI: 10.3390/s21186235
Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition for Decoding Perception of Faces Using Magnetoencephalography
Abstract
Neural decoding is useful to explore the timing and source location in which the brain encodes information. Higher classification accuracy means that an analysis is more likely to succeed in extracting useful information from noises. In this paper, we present the application of a nonlinear, nonstationary signal decomposition technique-the empirical mode decomposition (EMD), on MEG data. We discuss the fundamental concepts and importance of nonlinear methods when it comes to analyzing brainwave signals and demonstrate the procedure on a set of open-source MEG facial recognition task dataset. The improved clarity of data allowed further decoding analysis to capture distinguishing features between conditions that were formerly over-looked in the existing literature, while raising interesting questions concerning hemispheric dominance to the encoding process of facial and identity information.
Keywords: empirical mode decomposition (EMD); face perception; magnetoencephalography (MEG); neural decoding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


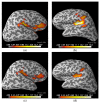
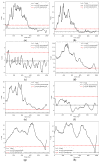

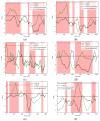
References
-
- Huang N.E., Shen Z., Long S.R., Wu M.C., Shih H.H., Zheng Q., Yen N.-C., Tung C.C., Liu H.H. The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-Stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998;454:903–995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193. - DOI

