A Study on the Classification Effect of sEMG Signals in Different Vibration Environments Based on the LDA Algorithm
- PMID: 34577443
- PMCID: PMC8469125
- DOI: 10.3390/s21186234
A Study on the Classification Effect of sEMG Signals in Different Vibration Environments Based on the LDA Algorithm
Abstract
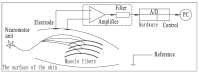
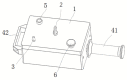
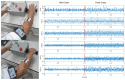
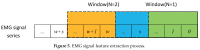
Myoelectric prosthesis has become an important aid to disabled people. Although it can help people to recover to a nearly normal life, whether they can adapt to severe working conditions is a subject that is yet to be studied. Generally speaking, the working environment is dominated by vibration. This paper takes the gripping action as its research object, and focuses on the identification of grasping intentions under different vibration frequencies in different working conditions. In this way, the possibility of the disabled people who wear myoelectric prosthesis to work in various vibration environment is studied. In this paper, an experimental test platform capable of simulating 0-50 Hz vibration was established, and the Surface Electromyography (sEMG) signals of the human arm in the open and grasping states were obtained through the MP160 physiological record analysis system. Considering the reliability of human intention recognition and the rapidity of algorithm processing, six different time-domain features and the Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) classifier were selected as the sEMG signal feature extraction and recognition algorithms in this paper. When two kinds of features, Zero Crossing (ZC) and Root Mean Square (RMS), were used as input, the accuracy of LDA algorithm can reach 96.9%. When three features, RMS, Minimum Value (MIN), and Variance (VAR), were used as inputs, the accuracy of the LDA algorithm can reach 98.0%. When the six features were used as inputs, the accuracy of the LDA algorithm reached 98.4%. In the analysis of different vibration frequencies, it was found that when the vibration frequency reached 20 Hz, the average accuracy of the LDA algorithm in recognizing actions was low, while at 0 Hz, 40 Hz and 50 Hz, the average accuracy was relatively high. This is of great significance in guiding disabled people to work in a vibration environment in the future.
Keywords: LDA algorithm; feature extraction; hand-motion recognition; surface EMG signal; vibration frequency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

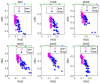
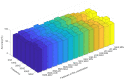

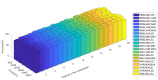
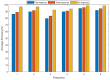
Similar articles
-
A motion-classification strategy based on sEMG-EEG signal combination for upper-limb amputees.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017 Jan 7;14(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12984-016-0212-z. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 28061779 Free PMC article.
-
NLR, MLP, SVM, and LDA: a comparative analysis on EMG data from people with trans-radial amputation.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017 Aug 14;14(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12984-017-0290-6. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 28807038 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous sEMG Classification of Hand/Wrist Gestures and Forces.Front Neurorobot. 2019 Jun 19;13:42. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2019.00042. eCollection 2019. Front Neurorobot. 2019. PMID: 31275131 Free PMC article.
-
Design of an Effective Prosthetic Hand System for Adaptive Grasping with the Control of Myoelectric Pattern Recognition Approach.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;13(2):219. doi: 10.3390/mi13020219. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35208342 Free PMC article.
-
Human Gait Recognition Based on Multiple Feature Combination and Parameter Optimization Algorithms.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021 Feb 27;2021:6693206. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693206. eCollection 2021. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33727913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CSAC-Net: Fast Adaptive sEMG Recognition through Attention Convolution Network and Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 11;22(10):3661. doi: 10.3390/s22103661. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35632069 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Stream Long Short-Term Memory Feature Fusion Classifier for Surface Electromyography Gesture Recognition.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;24(11):3631. doi: 10.3390/s24113631. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894423 Free PMC article.
-
Study on exercise muscle fatigue based on sEMG and ECG data fusion and temporal convolutional network.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 1;17(12):e0276921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276921. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36454887 Free PMC article.
-
Me-Doped Ti-Me Intermetallic Thin Films Used for Dry Biopotential Electrodes: A Comparative Case Study.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 6;21(23):8143. doi: 10.3390/s21238143. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34884159 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable Surface Electromyography System to Predict Freeze of Gait in Parkinson's Disease Patients.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 9;24(23):7853. doi: 10.3390/s24237853. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xing K., Yang P., Huang J., Wang Y., Zhu Q. A real-time EMG pattern recognition method for virtual myoelectric hand control. Neurocomputing. 2014;136:345–355. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.12.010. - DOI
-
- Carlucci F., Orlando G., Haxhi J., Laudani L., Giombini A., Macaluso A., Pigozzi F., Sacchetti M. Older Age Is Associated with Lower Optimal Vibration Frequency in Lower-Limb Muscles During Whole-Body Vibration. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015;94:522–529. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000193. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

