Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 34577602
- PMCID: PMC8468100
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14090902
Polydatin, a Glycoside of Resveratrol, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells In Vitro
Abstract
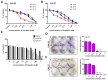
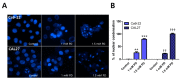
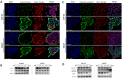
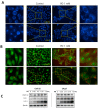
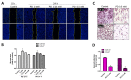
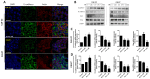
Although various methods, such as surgery and chemotherapy, are applied to the treatment of OSCC, there are problems, such as functional and aesthetic limitations of the mouth and face, drug side effects, and lymph node metastasis. Many researchers are making efforts to develop new therapeutic agents from plant-derived substances to overcome the side effects that occur in oral cancer treatment. Polydatin is known as a natural precursor of resveratrol, and research on its efficacy is being actively conducted recently. Therefore, we investigated whether polydatin can induce apoptosis and whether it affects cell migration and invasion through the regulation of EMT-related factors in OSCC. Polydatin decreased the survival and proliferation rates of CAL27 and Ca9-22 cells, and induced the release of cytochrome c, a factor related to apoptosis, and fragmentation of procaspase-3 and PARP. Another form of cell death, autophagy, was observed in polydatin-treated cells. In addition, polydatin inhibits cell migration and invasion, and it has been shown to occur through increased expression of E-cadherin, an EMT related factor, and decreased expression of N-cadherin and Slug and Snail proteins and genes. These findings suggest that polydatin is a potential oral cancer treatment.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; oral squamous cell carcinoma; polydatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polydatin Inhibits Cell Viability, Migration, and Invasion Through Suppressing the c-Myc Expression in Human Cervical Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 12;9:587218. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.587218. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33912552 Free PMC article.
-
KLF7 overexpression in human oral squamous cell carcinoma promotes migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncol Lett. 2017 Apr;13(4):2281-2289. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5734. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28454392 Free PMC article.
-
Polydatin, a natural precursor of resveratrol, induces cell cycle arrest and differentiation of human colorectal Caco-2 cell.J Transl Med. 2013 Oct 20;11:264. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-264. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 24138806 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Dietary Phytoestrogens on the Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Diverse Cancer Metastasis.Toxins (Basel). 2016 May 24;8(6):162. doi: 10.3390/toxins8060162. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27231938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities.Int J Cancer. 2021 Apr 1;148(7):1548-1561. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33352. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33091960 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathways in cancer angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by natural compounds: a comprehensive and critical review.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Mar;43(1):501-574. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10136-9. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 37792223 Review.
-
Resveratrol Inhibits Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) by Targeting the MAPK Signaling Pathway.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(16):1207-1219. doi: 10.2174/0118715206319761240705115109. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38988166
-
Chemopreventive and Anticancer Role of Resveratrol against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 13;15(1):275. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010275. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current nano drug delivery systems for targeting head and neck squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment: a narrative review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 8;52(1):369. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10462-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195238 Review.
-
Application of Natural Medicinal Plants Active Ingredients in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Sep;30(9):852-864. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3804-7. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38607612 Review.
References
-
- Hassanpour S.H., Dehghani M. Review of cancer from perspective of molecular. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017;4:127–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrpr.2017.07.001. - DOI
-
- Barabadi H., Hosseini O., Damavandi Kamali K., Jazayeri Shoushtari F., Rashedi M., Haghi-Aminjan H., Saravanan M. Emerging theranostic silver nanomaterials to combat lung cancer: A systematic review. J. Clust. Sci. 2020;31:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s10876-019-01639-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

