Potential and Limits of Kidney Cells for Evaluation of Renal Excretion
- PMID: 34577608
- PMCID: PMC8464824
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14090908
Potential and Limits of Kidney Cells for Evaluation of Renal Excretion
Abstract
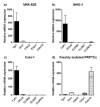
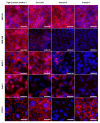
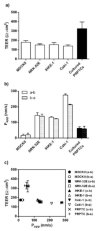
A large number of therapeutic drugs, herbal components and their metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, generally applied models for estimating renal excretion, including freshly isolated rat proximal tubule cells, cultured tubule cells and immortalized kidney cell lines MDCKII, NRK-52E, IHKE-1 and Caki-1, were investigated regarding their predictive potential for active renal transport. Cultured proximal tubule cells showed an epithelial cell-like morphology and formed tight monolayers. However, mRNA expression analyses and immunohistochemical studies revealed patterns of tight junction proteins that were notably different from freshly isolated cells and distinct from those in vivo. High levels of mannitol permeation were found in NRK-52E, IHKE-1 and Caki-1 cells, suggesting that they are not suitable for bidirectional transport studies. Cultured cells and freshly isolated cells also differed in proximal tubule markers and transport proteins, indicating that cultured primary cells were in a state of dedifferentiation. Cell lines MDCKII, NRK-52E, IHKE-1 and Caki-1 did not accurately reflect the characteristics of proximal tubules. The expression patterns of marker and transport proteins differed from freshly isolated primary cells. In summary, each of these models has profound disadvantages to consider when adopting them reliable models for the in vivo situation. Thus, they should not be used alone but only in combination.
Keywords: kidney cell lines; marker enzymes; renal excretion; transport proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



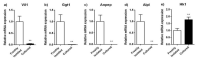

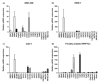

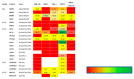
Similar articles
-
Epithelial barrier characteristics and expression of cell adhesion molecules in proximal tubule-derived cell lines commonly used for in vitro toxicity studies.Toxicol In Vitro. 2006 Sep;20(6):942-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2005.11.006. Epub 2006 Jan 4. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006. PMID: 16387471
-
Transcriptomes of Major Proximal Tubule Cell Culture Models.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jan;32(1):86-97. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020010009. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33122286 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study on the uptake of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid by normal and immortalized human embryonic kidney cells from proximal tubule.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 23;1190(2):279-88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90085-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994. PMID: 8142427
-
Chloride transporters and receptor-mediated endocytosis in the renal proximal tubule.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;593(18):4151-64. doi: 10.1113/JP270087. Epub 2015 May 11. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25820368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does membrane trafficking play a role in regulating the sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3 in the proximal tubule?Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003 Sep;12(5):533-41. doi: 10.1097/00041552-200309000-00009. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 12920402 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of cytotoxic agents or apoptosis stimulants on αklotho in MDCK, NRK-52E and HK2 kidney cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Aug 22;14(18):7282-7299. doi: 10.18632/aging.204238. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35997650 Free PMC article.
-
Caki-1 Spheroids as a Renal Model for Studying Free Fatty Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity.Cells. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):349. doi: 10.3390/cells14050349. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072078 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Analysis of a Pilot Transwell Barrier Model with Automated Sampling and Mathematical Modeling.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 20;15(11):2646. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112646. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004624 Free PMC article.
-
Human and rat renal proximal tubule in vitro models for ADME applications.Arch Toxicol. 2025 May;99(5):1613-1641. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-03987-4. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40032686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro technology and ADMET research in traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 9;16:1605330. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605330. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40703346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gildea J.J., Shah I., Weiss R., Casscells N.D., McGrath H.E., Zhang J., Jones J.E., Felder R.A. HK-2 Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells as a Model for G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase Type 4–Mediated Dopamine 1 Receptor Uncoupling. Hypertension. 2010;56:505–511. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.152256. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van der Hauwaert C., Savary G., Gnemmi V., Glowacki F., Pottier N., Bouillez A., Maboudou P., Zini L., Leroy X., Cauffiez C., et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Primary Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cell Model from Human Kidney by CD10/CD13 Double Labeling. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e66750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

