Design of a Hand-Held and Battery-Operated Digital Microfluidic Device Using EWOD for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications
- PMID: 34577709
- PMCID: PMC8466106
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12091065
Design of a Hand-Held and Battery-Operated Digital Microfluidic Device Using EWOD for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications
Abstract
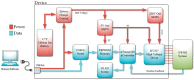
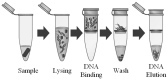
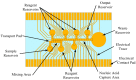
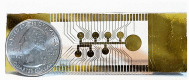
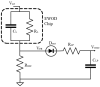
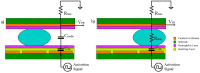
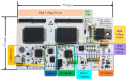
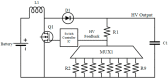
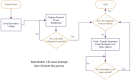
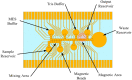
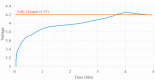
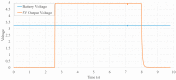
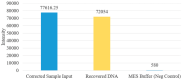
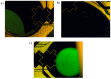
Microfluidics offer many advantages to Point of Care (POC) devices through lower reagent use and smaller size. Additionally, POC devices offer the unique potential to conduct tests outside of the laboratory. In particular, Electro-wetting on Dielectric (EWOD) microfluidics has been shown to be an effective way to move and mix liquids enabling many PoC devices. However, much of the research surrounding these microfluidic systems are focused on a single aspect of the system capability, such as droplet control or a specific new application at the device level using the EWOD technology. Often in these experiments the supporting systems required for operation are bench top equipment such as function generators, power supplies, and personal computers. Although various aspects of how an EWOD device is capable of moving and mixing droplets have been demonstrated at various levels, a complete self-contained and portable lab-on-a-chip system based on the EWOD technology has not been well demonstrated. For instance, EWOD systems tend to use high voltage alternating current (AC) signals to actuate electrodes, but little consideration is given to circuitry size or power consumption of such components to make the entire system portable. This paper demonstrates the feasibility of integrating all supporting hardware and software to correctly operate an EWOD device in a completely self-contained and battery-powered handheld unit. We present results that demonstrate a complete sample preparation flow for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction and isolation. The device was designed to be a field deployable, hand-held platform capable of performing many other sample preparation tasks automatically. Liquids are transported using EWOD and controlled via a programmable microprocessor. The programmable nature of the device allows it to be configured for a variety of tests for different applications. Many considerations were given towards power consumption, size, and system complexity which make it ideal for use in a mobile environment. The results presented in this paper show a promising step forward to the portable capability of microfluidic devices based on the EWOD technology.
Keywords: Electro-wetting on Dielectric (EWOD); Point of Care (POC); digital microfluidics (DMF); lab on chip (LOC); sample preparation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extraction of Cell-free Dna from An Embryo-culture Medium Using Micro-scale Bio-reagents on Ewod.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 16;10(1):9708. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66779-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32546702 Free PMC article.
-
A Low-Cost, Disposable and Portable Inkjet-Printed Biochip for the Developing World.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 25;20(12):3593. doi: 10.3390/s20123593. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630509 Free PMC article.
-
Solution for Mass Production of High-Throughput Digital Microfluidic Chip Based on a-Si TFT with In-Pixel Boost Circuit.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Sep 30;12(10):1199. doi: 10.3390/mi12101199. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34683251 Free PMC article.
-
Electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): Current perspectives and applications in ensuring food safety.J Food Drug Anal. 2020 Dec 15;28(4):595-621. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.1239. J Food Drug Anal. 2020. PMID: 35696148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining sensors and actuators with electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): advanced digital microfluidic systems for biomedical applications.Analyst. 2023 Mar 27;148(7):1399-1421. doi: 10.1039/d2an01707e. Analyst. 2023. PMID: 36752059 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of Transparent and Flexible Digital Microfluidics Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;13(4):498. doi: 10.3390/mi13040498. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35457803 Free PMC article.
-
Colorimetric Sensing with Gold Nanoparticles on Electrowetting-Based Digital Microfluidics.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;12(11):1423. doi: 10.3390/mi12111423. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832834 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Sided Tape in Microfluidics: A Cost-Effective Method in Device Fabrication.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 15;14(5):249. doi: 10.3390/bios14050249. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DBSCAN-PCA-INFORMER-Based Droplet Motion Time Prediction Model for Digital Microfluidic Systems.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 May 19;16(5):594. doi: 10.3390/mi16050594. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428720 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Electrode Patterns for an ITO-Based Digital Microfluidic through the Finite Element Simulation.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;13(10):1563. doi: 10.3390/mi13101563. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren H., Fair R.B., Pollack M.G. Automated on-chip droplet dispensing with volume control by electro-wetting actuation and capacitance metering. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004;98:319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2003.09.030. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

