Influence of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection on the Course of Psoriasis during Treatment with Biological Drugs
- PMID: 34577804
- PMCID: PMC8470849
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57090881
Influence of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection on the Course of Psoriasis during Treatment with Biological Drugs
Abstract
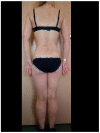
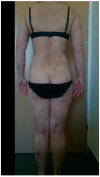
Background and objectives: Biological treatment is an important and effective therapy for psoriasis. During the COVID-19 pandemic, it remains unclear whether this type of therapy affects the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aim of the study was to observe patients with psoriasis undergoing biological or other systemic treatment in relation to the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the course of psoriasis and the COVID-19 disease itself. Materials and methods: A one-year observational study included 57 patients with diagnosed psoriasis who qualified for biological treatment and a group of 68 similar patients who were administered a different systemic treatment. Patients were analyzed monthly for psoriasis (including Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) assessment) and constantly for SARS-CoV-2 infection (telephone contact). Cases of COVID-19 were confirmed by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) at the study center. Results: SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed by a positive Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test in eight patients (14.0%) with psoriasis on biological therapy. None of the cases in this group required hospitalization for COVID-19. Similar data were obtained in the control group. Specifically, 11 (16%) patients were confirmed to be infected with SARS-CoV-2. These results were statistically comparable (p > 0.05). In the group of patients undergoing biological treatment, six (75%) of eight patients developed an exacerbation of psoriasis during SARS-CoV-2 infection, and similar results were noted in the control group, with eight (72%) patients experiencing an exacerbation of psoriasis. Conclusions: Patients with psoriasis who were administered biological treatment or other systemic therapy may experience a mild course of SARS-CoV-2 infection but might also experience a temporary exacerbation of skin lesions.
Keywords: COVID-19; biological drugs; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT OF PSORIASIS IN TIME OF NEW CORONAVIRUS INFECTION COVID-19].Probl Sotsialnoi Gig Zdravookhranenniiai Istor Med. 2021 Aug;29(Special Issue):1381-1387. doi: 10.32687/0869-866X-2021-29-s2-1381-1387. Probl Sotsialnoi Gig Zdravookhranenniiai Istor Med. 2021. PMID: 34792893 Russian.
-
The prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the course of COVID-19 in patients with psoriasis treated with biologic therapy.J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 May;33(3):1581-1584. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1861177. Epub 2020 Dec 22. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022. PMID: 33317364
-
Characteristic of chronic plaque psoriasis patients treated with biologics in Italy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Risk analysis from the PSO-BIO-COVID observational study.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021 Feb;21(2):271-277. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1853698. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33216643
-
COVID-19 and psoriasis: biologic treatment and challenges.J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 Mar;33(2):699-703. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1789051. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022. PMID: 32598204 Review.
-
Use of biologics during the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons learned from psoriasis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022 Dec;22(12):1521-1529. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2110467. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35930356 Review.
Cited by
-
Types of Psoriasis and Their Effects on the Immune System.Cureus. 2022 Sep 24;14(9):e29536. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29536. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36312680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin Manifestations in Psoriatic and HS Patients in Treatment with Biologicals during the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 13;10(24):5841. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245841. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Braun-Falco O., Burgdorf W.H.C., Plewig G., Wolff H.H., Landthaler M. Psoriasis. 3rd ed. Springer; Heidelberg, Germany: 2009. Dermatology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous