Responsive Quaternized PDMAEMA Copolymers with Antimicrobial Action
- PMID: 34577950
- PMCID: PMC8472408
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13183051
Responsive Quaternized PDMAEMA Copolymers with Antimicrobial Action
Abstract
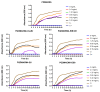
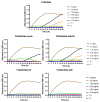
In this work, the antimicrobial action of partially quaternized poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PQDMAEMA) copolymers using different alkyl halides is presented. The poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) homopolymer was synthesized by group transfer polymerization, followed by the modification of its tertiary amine groups, using bromoethane, iodoethane, bromohexane and bromoethanol, to introduce permanent cationic, quaternary ammonium salt moieties, randomly distributed along the polymer chains. In all cases, the degree of quaternization was low, at ~10 mol%, as verified by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to preserve the thermo-responsive character of the PDMAEMA precursor polymer. The biocidal activity of the lightly quaternized PQDMAEMA copolymers against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated by calculating the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) as well as the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of the polymers and by comparing them to the respective values of the precursor non-quaternized PDMAEMA homopolymer. The antibacterial mechanism of action in the solution was studied by zeta potential measurements, scanning electron microscopy and protein leakage tests signifying the disruption of the outer membrane of the bacterial cells to release their periplasmic proteins.
Keywords: E. coli; MBC; MIC; PDMAEMA; S. aureus; antimicrobial polymers; minimum bactericidal concentration; minimum inhibitory concentration; quaternization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A facile route towards PDMAEMA homopolymer amphiphiles.Soft Matter. 2017 May 24;13(20):3777-3782. doi: 10.1039/c7sm00365j. Soft Matter. 2017. PMID: 28480930
-
Film Properties and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Quaternized PDMAEMA Brushes: Short vs Long Alkyl Chain Length.Langmuir. 2020 Apr 7;36(13):3482-3493. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03266. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Langmuir. 2020. PMID: 32168453
-
Antibacterial cellulose fiber via RAFT surface graft polymerization.Biomacromolecules. 2008 Jan;9(1):91-9. doi: 10.1021/bm700849j. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Biomacromolecules. 2008. PMID: 18067264
-
Polyelectrolyte complexes between (cross-linked) N-carboxyethylchitosan and (quaternized) poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate]: preparation, characterization, and antibacterial properties.Biomacromolecules. 2007 Mar;8(3):976-84. doi: 10.1021/bm061029j. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Biomacromolecules. 2007. PMID: 17315947
-
Nonleaching antibacterial glass surfaces via "Grafting Onto": the effect of the number of quaternary ammonium groups on biocidal activity.Langmuir. 2008 Jun 1;24(13):6785-95. doi: 10.1021/la8003933. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Langmuir. 2008. PMID: 18517227
Cited by
-
Bactericidal Anti-Adhesion Potential Integrated Polyoxazoline/Silver Nanoparticle Composite Multilayer Film with pH Responsiveness.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 5;14(17):3685. doi: 10.3390/polym14173685. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080760 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(vinyl pyridine) and Its Quaternized Derivatives: Understanding Their Solvation and Solid State Properties.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;14(4):804. doi: 10.3390/polym14040804. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215717 Free PMC article.
-
Microphase Separation of Poly(2-(Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate)-b-Poly(Tetrahydropyranyl Methacrylate) Diblock Copolymer Thin Films.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025 Aug;46(15):e2500138. doi: 10.1002/marc.202500138. Epub 2025 May 11. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025. PMID: 40350973 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Environmentally Friendly Biocidal Coatings Based on Water-soluble Copolymers for Air-cleaning Filters.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 19;7(39):35204-35216. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04427. eCollection 2022 Oct 4. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36211061 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "State-of-the-Art Polymer Science and Technology in Greece".Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;15(5):1264. doi: 10.3390/polym15051264. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lorenzo J.M., Munekata P.E., Dominguez R., Pateiro M., Saraiva J.A., Franco D. Chapter 3—Main Groups of Microorganisms of Relevance for Food Safety and Stability: General Aspects and Overall Description. In: Barba F.J., Sant’Ana A.S., Orlien V., Koubaa M., editors. Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2018. pp. 53–107.
-
- Rennie R.P. Current and Future Challenges in the Development of Antimicrobial Agents. In: Coates A.R.M., editor. Antibiotic Resistance. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. pp. 45–65. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

