A Hierarchical Grid Solver for Simulation of Flows of Complex Fluids
- PMID: 34578066
- PMCID: PMC8471049
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13183168
A Hierarchical Grid Solver for Simulation of Flows of Complex Fluids
Abstract
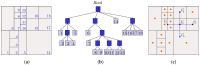
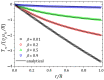
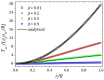
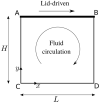
Tree-based grids bring the advantage of using fast Cartesian discretizations, such as finite differences, and the flexibility and accuracy of local mesh refinement. The main challenge is how to adapt the discretization stencil near the interfaces between grid elements of different sizes, which is usually solved by local high-order geometrical interpolations. Most methods usually avoid this by limiting the mesh configuration (usually to graded quadtree/octree grids), reducing the number of cases to be treated locally. In this work, we employ a moving least squares meshless interpolation technique, allowing for more complex mesh configurations, still keeping the overall order of accuracy. This technique was implemented in the HiG-Flow code to simulate Newtonian, generalized Newtonian and viscoelastic fluids flows. Numerical tests and application to viscoelastic fluid flow simulations were performed to illustrate the flexibility and robustness of this new approach.
Keywords: finite difference methods; meshless interpolation; numerical solution; polymer flows; viscoelastic flows.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Berger M.J., Oliger J. Adaptive mesh refinement for hyperbolic partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1984;53:484–512. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(84)90073-1. - DOI
-
- Popinet S. Gerris: A tree-based adaptive solver for the incompressible Euler equations in complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 2003;190:572–600. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00298-5. - DOI
-
- Losasso F., Gibou F., Fedkiw R. Simulating Water and Smoke with an Octree Data Structure. ACM Trans. Graph. 2004;23:457–462. doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015745. - DOI
-
- Olshanskii M.A., Terekhov K.M., Vassilevski Y.V. An octree-based solver for the incompressible Navier Stokes equations with enhanced stability and low dissipation. Comput. Fluids. 2013;84:231–246. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.04.027. - DOI
-
- Guittet A., Theillard M., Gibou F. A stable projection method for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations on arbitrary geometries and adaptive Quad/Octrees. J. Comput. Phys. 2015;292:215–238. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.03.024. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 0050.0075367.12.9/Petrobras
- 2013/07375-0, 2017/21105-6 and 2020/02990-1./Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 307483/2017-7/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- PTDC/EMS-ENE/3362/2014, POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016665, UIDB/00013/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

