Preparation of a Hydrogel Nanofiber Wound Dressing
- PMID: 34578494
- PMCID: PMC8465883
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11092178
Preparation of a Hydrogel Nanofiber Wound Dressing
Abstract
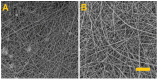
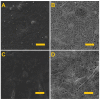
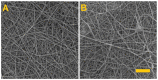
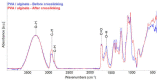
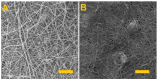
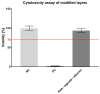
The study addressed the production of a hydrogel nanofiber skin cover and included the fabrication of hydrogel nanofibers from a blend of polyvinyl alcohol and alginate. The resulting fibrous layer was then crosslinked with glutaraldehyde, and, after 4 h of crosslinking, although the gelling component, i.e., the alginate, crosslinked, the polyvinyl alcohol failed to do so. The experiment included the comparison of the strength and ductility of the layers before and after crosslinking. It was determined that the fibrous layer following crosslinking evinced enhanced mechanical properties, which acted to facilitate the handling of the material during its application. The subsequent testing procedure proved that the fibrous layer was not cytotoxic. The study further led to the production of a modified hydrogel nanofiber layer that combined polyvinyl alcohol with alginate and albumin. The investigation of the fibrous layers produced determined that following contact with water the polyvinyl alcohol dissolved leading to the release of the albumin accompanied by the swelling of the alginate and the formation of a hydrogel.
Keywords: alginate; hydrogel; nanofibers; polyvinyl alcohol; skin cover.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ghomi E.R., Khalili S., Khorasani S.N., Neisiany R.E., Ramakrishna S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019;136:47738. doi: 10.1002/app.47738. - DOI
-
- Kirwan H., Pignataro R. Chapter 2-The Skin and Wound Healing. In: Magee D.J., Zachazewski J.E., Quillen W.S., Manske R.C., editors. Pathology and Intervention in Musculoskeletal Re-Habilitation. 2nd ed. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2016. pp. 25–62.
-
- Mayandi V., Choong A.C.W., Dhand C., Lim F.P., Aung T.T., Sriram H., Dwivedi N., Periayah M.H., Sridhar S., Fazil M.H.U.T., et al. Multifunctional Antimicrobial Nanofiber Dressings Containing ε-Polylysine for the Eradication of Bacterial Bioburden and Promotion of Wound Healing in Critically Colonized Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020;12:15989–16005. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b21683. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schoukens G. 5-Bioactive dressings to promote wound healing. In: Rajendran S., editor. Advanced Textiles for Wound Care. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2009. pp. 114–152. (Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

