The Med-NKQ: A Reliable Mediterranean Diet Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire for Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 34578825
- PMCID: PMC8471340
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13092949
The Med-NKQ: A Reliable Mediterranean Diet Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
The Mediterranean diet (MD) has significant benefits for cardiovascular disease (CVD), yet clinicians lack reliable tools to measure patient knowledge. This study aimed to develop a short tool to test knowledge of MD related to cardiac health. Themes included foods to reduce CVD risk factors, quantification of servings, and common MD dietary patterns; a maximum score of 42 was determined for correct responses. Content validity was assessed through expert consensus in a Delphi survey. A 70% level of agreement was set for each domain tested. Repeatability was assessed via a test-retest protocol in a sample with self-reported CVD, advertised through social media and administered online. Ten and six of twenty-five invited experts responded to round one and two of the Delphi survey respectively. All items achieved greater than 70% consensus. Twenty people completed the repeatability study. A paired t-test found no significant difference in mean scores between the two test periods (Test one, 28 (standard deviation (SD) 5.4). Test two 29.5, (SD 5.5), p = 0.174) and a Bland-Altman Plot indicated no bias between the two surveys. The Med-NKQ demonstrated good content validity and reliability in people with CVD, and is short and easy to administer, making it practical in clinical and research settings.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; delphi; mediterranean diet; nutrition knowledge; repeatability; survey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
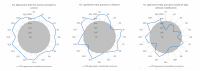

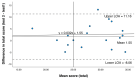
References
-
- World Health Organisation Cardiovascular Diseases. [(accessed on 28 November 2018)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-...
-
- National Vascular Disease Prevention Alliance . Guidelines for the Management of Absolute Cardiovascular Disease Risk. National Vascular Disease Prevention Alliance; Australia: 2012.
-
- Artinian N.T., Fletcher G.F., Mozaffarian D., Kris-Etherton P., Van Horn L., Lichtenstein A.H., Kumanyika S., Kraus W.E., Fleg J.L., Redeker N.S., et al. Interventions to promote physical activity and dietary lifestyle changes for cardiovascular risk factor reduction in adults: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;122:406–441. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181e8edf1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Lorgeril M., Salen P., Martin J.L., Monjaud I., Delaye J., Mamelle N. Mediterranean diet, traditional risk factors, and the rate of cardiovascular complications after myocardial infarction: Final report of the Lyon Diet Heart Study. Circulation. 1999;99:779–785. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.99.6.779. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Estruch R., Ros E., Salas-Salvado J., Covas M.I., Corella D., Aros F., Gomez-Gracia E., Ruiz-Gutierrez V., Fiol M., Lapetra J., et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:e34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800389. - DOI - PubMed
