Association of Serum Vitamin B6 with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Prospective Study
- PMID: 34578855
- PMCID: PMC8472743
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13092977
Association of Serum Vitamin B6 with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Prospective Study
Abstract
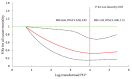
There is little evidence regarding the association between serum vitamin B6 concentration and subsequent mortality. We aimed to evaluate the association of serum vitamin B6 concentration with all-cause, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and cancer mortality in the general population using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Our study examined 12,190 adults participating in NHANES from 2005 to 2010 in the United States. The mortality status was linked to National Death Index (NDI) records up to 31 December 2015. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) is the biologically active form of vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 status was defined as deficient (PLP < 20 nmol/L), insufficient (PLP ≥ 20.0 and <30.0 nmol/L), and sufficient (PLP ≥ 30.0 nmol/L). We established Cox proportional-hazards models to estimate the associations of categorized vitamin B6 concentration and log-transformed PLP concentration with all-cause and cause-specific mortality by calculating hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs). In our study, serum vitamin B6 was sufficient in 70.6% of participants, while 12.8% of the subjects were deficient in vitamin B6. During follow-up, a total of 1244 deaths were recorded, including 294 cancer deaths and 235 CVD deaths. After multivariate adjustment in Cox regression, participants with higher serum vitamin B6 had a 15% (HR = 0.85, 95%CI = 0.77, 0.93) reduced risk of all-cause mortality and a 19% (HR = 0.81, 95%CI = 0.68, 0.98) reduced risk for CVD mortality for each unit increment in natural log-transformed PLP. A higher log-transformed PLP was not significantly associated with a lower risk for cancer mortality. Compared with sufficient vitamin B6, deficient (HR = 1.37, 95%CI = 1.17, 1.60) and insufficient (HR = 1.19, 95%CI = 1.02, 1.38) vitamin B6 level were significantly associated with a higher risk for all-cause mortality. There was no significant association for cause-specific mortality. Participants with higher levels of vitamin B6 had a lower risk for all-cause mortality. These findings suggest that maintaining a sufficient level of serum vitamin B6 may lower the all-cause mortality risk in the general population.
Keywords: NHANES; mortality; pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP); serum; vitamin B6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of serum vitamin B6 status with the risks of cardiovascular, cancer, and all-cause mortality in the elderly.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1354958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354958. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38698865 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of vitamin B6 turnover rate with the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in hypertensive adults.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Jun;33(6):1225-1234. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.03.017. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37085414
-
Vitamin B6 status, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and periodontitis: evidence from the NHANES database 2009-2010.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Feb 24;25(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05597-z. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39994649 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of vitamin D status to risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality.Dan Med J. 2015 Feb;62(2):B5008. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25634511 Review.
-
Consumption of dairy product and its association with total and cause specific mortality - A population-based cohort study and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr. 2019 Dec;38(6):2833-2845. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30595374
Cited by
-
Relationship of Low Vitamin B6 Status with Sarcopenia, Frailty, and Mortality: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):177. doi: 10.3390/nu16010177. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38202006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of serum vitamin B6 status with the risks of cardiovascular, cancer, and all-cause mortality in the elderly.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1354958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354958. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38698865 Free PMC article.
-
Pyridoxine Deficiency and Neurologic Dysfunction: An Unlikely Association.Cureus. 2023 Oct 25;15(10):e47647. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47647. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021490 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum pyridoxal 5'-phosphate levels and all-cause, cardiovascular mortality, and cardiovascular disease in adults: a population-based cohort study.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024 Oct 18;15:20406223241290411. doi: 10.1177/20406223241290411. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2024. PMID: 39429976 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary vitamin B6 intake and stroke are negatively associated in adults: A cross-sectional study from the NHANES.Heliyon. 2024 May 11;10(10):e31125. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31125. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38778939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Nutrition Report 2017: Nourishing the SDGs. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013.
-
- Pfeiffer C.M., Sternberg M.R., Schleicher R.L., Haynes B.M., Rybak M.E., Pirkle J.L. The CDC’s Second National Report on Biochemical Indicators of Diet and Nutrition in the U.S. Population is a valuable tool for researchers and policy makers. J. Nutr. 2013;143:938s–947s. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.172858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agnoli C., Grioni S., Krogh V., Pala V., Allione A., Matullo G., Di Gaetano C., Tagliabue G., Pedraglio S., Garrone G., et al. Plasma Riboflavin and Vitamin B-6, but Not Homocysteine, Folate, or Vitamin B-12, Are Inversely Associated with Breast Cancer Risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition-Varese Cohort. J. Nutr. 2016;146:1227–1234. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.225433. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials