Lower Levels of Vitamin D Are Associated with an Increase in Insulin Resistance in Obese Brazilian Women
- PMID: 34578857
- PMCID: PMC8471993
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13092979
Lower Levels of Vitamin D Are Associated with an Increase in Insulin Resistance in Obese Brazilian Women
Abstract
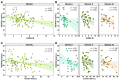
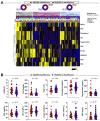
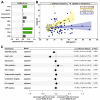
Adult women are more likely to be obese than men. Moreover, there is evidence that obesity is a risk factor for increased insulin resistance (IR) and hypovitaminosis D (VITD), conditions related to metabolic and endocrinologic disturbance. We performed a cross-sectional study with 103 women diagnosed with obesity, recruited between 2009 and 2013, in an obesity referral outpatient clinic in Bahia, Brazil. Laboratory and clinical characteristics were compared between the groups according to the degree of obesity (I, II and III), and levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] were used to define the VITD status (insufficiency and no insufficiency). We calculated the homeostatic model assessment-IR (HOMA-IR) index to assess insulin resistance in the groups. Our analyses revealed that HOMA-IR values and VITD levels were inversely correlated. Furthermore, we observed a distinct expression profile of values of laboratory markers according to 25(OH)D levels. Negative correlations were found between HOMA-IR and body mass index (BMI) in VITD insufficient participants but not in those with the sufficiency. Furthermore, multivariate regression demonstrated independent associations between lower levels of 25(OH)D and increased values of HOMA-IR. These findings suggests that lower levels of VITD are strongly associated with the increased IR in obese women.
Keywords: HOMA-IR; insulin resistance; obesity; vitamin D; women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 1 July 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Um Em Cada Quatro Adultos Do País Estava Obeso Em 2019. [(accessed on 8 June 2021)]; Available online: https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/agencia-noticias/2012-agencia-de-n....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

