Influence of Healthy Habits Counseling on Biochemical and Metabolic Parameters in Children and Adolescents with HIV: Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 34579114
- PMCID: PMC8466268
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13093237
Influence of Healthy Habits Counseling on Biochemical and Metabolic Parameters in Children and Adolescents with HIV: Longitudinal Study
Abstract
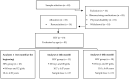
We analyze the influence of dietary counseling and physical activity on biochemical and metabolic parameters in children and adolescents with HIV. A longitudinal experimental study, including three analyses: At the beginning, 4th month, and 8th month. A sample of 18 subjects with HIV of both sexes, mean age 10.4 ± 4.50 years. Usual food intake (24 h recall and food intake marker), level of habitual physical activity, biochemical parameters, resting metabolic rate, as well as body composition (dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry), biological maturation, and anamnesis with clinical data and socioeconomic were evaluated. There was an effect of time on the reduction of blood glucose and triglycerides and the resting metabolic rate. There was a significant increase in fruit consumption throughout the study. The consumption of soft drinks decreased when comparing analysis periods 1 and 2, however, it increased again in analysis period 3. There was no significant effect of time on the set of variables related to a food recall. Counseling healthy habits and regular clinical follow-up were relevant for improving biochemical parameters (glucose, triglyceride, HDL cholesterol), maintaining the resting metabolic rate, increasing fruit consumption, and decreasing the consumption of soft drinks, in part of the time, of children and adolescents with HIV. Finally, we emphasize that counseling positively influenced healthy habits, and these, in turn, improved health-related parameters.
Keywords: HIV; nutrition; physical activity; young.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
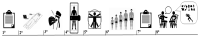
Similar articles
-
[Simple obesity in children. A study on the role of nutritional factors].Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006 Jan-Mar;10(1):3-191. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2006. PMID: 16733288 Review. Polish.
-
Body composition and metabolic effects of a diet and exercise weight loss regimen on obese, HIV-infected women.Metabolism. 2006 Oct;55(10):1327-36. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2006.05.018. Metabolism. 2006. PMID: 16979403
-
[Longitudinal changes in body composition and basal metabolic rate in institutionalized or domiciled obese adolescents].Arch Pediatr. 2005 Sep;12(9):1349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2005.04.077. Arch Pediatr. 2005. PMID: 15946831 French.
-
Impact of Vigorous-Intensity Physical Activity on Body Composition Parameters, Lipid Profile Markers, and Irisin Levels in Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 11;12(3):742. doi: 10.3390/nu12030742. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32168929 Free PMC article.
-
Beverage intake among preschool children and its effect on weight status.Pediatrics. 2006 Oct;118(4):e1010-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-2348. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 17015497
Cited by
-
The default mode network is affected in the early stage of simian immunodeficiency virus infection: a longitudinal study.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jul;18(7):1542-1547. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.360244. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36571360 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Physical Fitness Evaluation in HIV-Diagnosed Children and Adolescents: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Apr 25;21(5):541. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21050541. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38791753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Baros Ramalho L.C., Gonçalves E., de Carvalho W.R.G., Guerra-Junior G., Centeville M., Aoki F.H., Morcillo A., Vilela M.M.D.S., da Silva M.T.N. Abnormalities in body composition and nutritional status in HIV-infected children and adolescents on antiretroviral therapy. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2011;22:453–456. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2011.010516. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown R.J., Araujo-Vilar D., Cheung P.T., Dunger P.D., Garg A., Jack M., Mungai L., Oral E.A., Patni N., Rother K.I., et al. The diagnosis and management of lipodystrophy syndromes: A multi-society practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101:4500–4511. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-2466. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

