Qualitative Assessment of Early Adverse Effects of Pfizer-BioNTech and Sinopharm COVID-19 Vaccines by Telephone Interviews
- PMID: 34579187
- PMCID: PMC8473339
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9090950
Qualitative Assessment of Early Adverse Effects of Pfizer-BioNTech and Sinopharm COVID-19 Vaccines by Telephone Interviews
Abstract
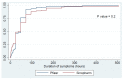
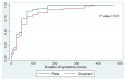
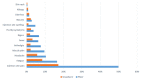
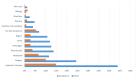
Vaccines are considered the best approach for countering the COVID-19 pandemic. In this study, we compared early side effects associated with vaccination with the Sinopharm and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines. Participants of this observational cohort were interviewed based on semi-structured telephone interviews, with enquiries about side effects that developed after vaccination with each dose of these vaccines. Overall, 1004 participants were enrolled, of which 51.1% received Sinopharm vaccine and 48.9% received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. After the first dose, 46.3% of participants had an adverse reaction, with injection site pain most commonly being reported (33.2%). Participants who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had significantly higher frequencies of all types of adverse reactions (p < 0.01), with no significant differences in the duration of adverse reactions between the two vaccines. Regarding the second dose, 48.6% of participants had adverse reactions, with injection site pain being most commonly reported (29%). Those who received the Pfizer vaccine reported higher frequencies of all adverse reactions (p < 0.01). However, a longer duration of adverse reactions was seen among Sinopharm vaccine recipients as compared to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients (p = 0.01). In conclusion, early adverse effects are reported following all types of vaccines but these are more likely to be encountered following the administration of new-generation vaccines. These side effects are mostly mild and treatable.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pfizer–BioNTech; Sinopharm; pandemic; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ratan Z.A., Hosseinzadeh H., Runa N.J., Mahtab Uddin B.M., Haidere M.F., Sarker S.K., Bin Zaman S. Novel Coronavirus: A new challenge for medical scientist? Bangladesh J. Infect. Dis. 2020;7:S58–S60. doi: 10.3329/bjid.v7i0.46805. - DOI
-
- Gopinathan U., Peacocke E., Gouglas D., Ottersen T., Røttingen J.-A. Infectious Diseases in the New Millennium. Springer; London, UK: 2020. R&D for Emerging Infectious Diseases of Epidemic Potential: Sharing Risks and Benefits Through a New Coalition; pp. 137–165.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

