Randomized Phase II Study of PARP Inhibitor ABT-888 (Veliparib) with Modified FOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI as Second-line Treatment of Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: SWOG S1513
- PMID: 34580114
- PMCID: PMC8639715
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1789
Randomized Phase II Study of PARP Inhibitor ABT-888 (Veliparib) with Modified FOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI as Second-line Treatment of Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: SWOG S1513
Abstract
Purpose: PARP inhibitors synergize with topoisomerase inhibitors, and veliparib plus modified (m) FOLFIRI (no 5-FU bolus) had preliminary activity in metastatic pancreatic cancers. This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of second-line treatment with veliparib and mFOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI (control) for metastatic pancreatic cancer.
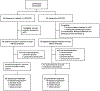
Patients and methods: This randomized phase II clinical trial led by the SWOG Cancer Research Network enrolled patients between September 1, 2016 and December 13, 2017. The median follow-up was 9 months (IQR 1-27). BRCA1/2 and homologous recombination DNA damage repair (HR-DDR) genetic defects were tested in blood and tumor biopsies. Patients received veliparib 200 mg twice daily, days 1-7 with mFOLFIRI days 3-5, or FOLFIRI in 14-day cycles.
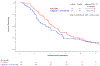
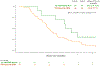
Results: After 123 of planned 143 patients were accrued, an interim futility analysis indicated that the veliparib arm was unlikely to be superior to control, and the study was halted. Median overall survival (OS) was 5.4 versus 6.5 months (HR, 1.23; P = 0.28), and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 2.1 versus 2.9 months (HR, 1.39; P = 0.09) with veliparib versus control. Grade 3/4 toxicities were more common with veliparib (69% vs. 58%, P = 0.23). For cancers with HR-DDR defects versus wild-type, median PFS and OS were 7.3 versus 2.5 months (P = 0.05) and 10.1 versus 5.9 months (P = 0.17), respectively, with FOLFIRI, and 2.0 versus 2.1 months (P = 0.62) and 7.4 versus 5.1 months (P = 0.10), respectively, with veliparib plus mFOLFIRI.
Conclusions: Veliparib plus mFOLFIRI did not improve survival for metastatic pancreatic cancer. FOLFIRI should be further studied in pancreatic cancers with HR-DDR defects.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
Figures





Comment on
-
Selected Articles from This Issue.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 1;27(23):6279. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-27-23-HI. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34853073 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 7–33. - PubMed
-
- Wang-Gillam A, Hubner RA, Siveke JT, Von Hoff DD, Belanger B, de Jong FA, et al. NAPOLI-1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long-term survivors. Eur J Cancer 2019; 108: 78–87. - PubMed
-
- Holter S, Borgida A, Dodd A, Grant R, Semotiuk K, Hedley D, et al. Germline BRCA mutations in a large clinic-based cohort of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 3124–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180826/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233230/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189830/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189856/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189960/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189971/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180834/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA190002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233324/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189809/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA239767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189957/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

