HPV Sequencing Facilitates Ultrasensitive Detection of HPV Circulating Tumor DNA
- PMID: 34580115
- PMCID: PMC9401563
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2384
HPV Sequencing Facilitates Ultrasensitive Detection of HPV Circulating Tumor DNA
Abstract
Purpose: Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA offers a convenient circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) marker for HPV-associated malignancies, but current methods, such as digital PCR (dPCR), provide insufficient accuracy for clinical applications in patients with low disease burden. We asked whether a next-generation sequencing approach, HPV sequencing (HPV-seq), could provide quantitative and qualitative assessment of HPV ctDNA in low disease burden settings.
Experimental design: We conducted preclinical technical validation studies on HPV-seq and applied it retrospectively to a prospective multicenter cohort of patients with locally advanced cervix cancer (NCT02388698) and a cohort of patients with oropharynx cancer. HPV-seq results were compared with dPCR. The primary outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) according to end-of-treatment HPV ctDNA detectability.
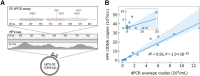
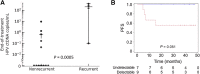
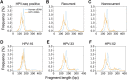
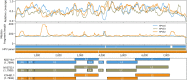
Results: HPV-seq achieved reproducible detection of HPV DNA at levels less than 0.6 copies in cell line data. HPV-seq and dPCR results for patients were highly correlated (R 2 = 0.95, P = 1.9 × 10-29) with HPV-seq detecting ctDNA at levels down to 0.03 copies/mL plasma in dPCR-negative posttreatment samples. Detectable HPV ctDNA at end-of-treatment was associated with inferior PFS with 100% sensitivity and 67% specificity for recurrence. Accurate HPV genotyping was successful from 100% of pretreatment samples. HPV ctDNA fragment sizes were consistently shorter than non-cancer-derived cell-free DNA (cfDNA) fragments, and stereotyped cfDNA fragmentomic patterns were observed across HPV genomes.
Conclusions: HPV-seq is a quantitative method for ctDNA detection that outperforms dPCR and reveals qualitative information about ctDNA. Our findings in this proof-of-principle study could have implications for treatment monitoring of disease burden in HPV-related cancers. Future prospective studies are needed to confirm that patients with undetectable HPV ctDNA following chemoradiotherapy have exceptionally high cure rates.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
![Figure 1. Overview of HPV-seq and dual-strand hybrid capture. A, HPV-seq conducted on plasma cfDNA is designed to provide quantitative and qualitative information about ctDNA in patients with HPV-associated cancers. In addition to being highly sensitive and quantitative, HPV-seq can report on ctDNA fragment size and HPV genotype. Each full-length viral genome (episome or linearized genome) is expected to yield approximately 50 distinct cfDNA fragments. B, HPV-seq is conducted using hybrid-capture sequencing with single-stranded [sense (+) and/or antisense (−)] biotinylated baits tiled across the HPV genome: (i) single-strand viral genome hybrid capture, (ii) sequential dual-strand hybrid capture, and (iii) simultaneous dual-strand hybrid capture. C, Compared with single-strand hybrid capture (i), dual-strand hybrid capture using either a sequential (ii) or simultaneous (iii) approach recovers more HPV molecules. Results were normalized to the degree of HPV sequence enrichment with a single round of capture using single-stranded baits (left-most bar). Subjecting the unbound library to another round of hybrid capture using baits targeting the same strand (second bar from left) did not improve HPV sequence enrichment. The degree of HPV DNA enrichment in postcapture libraries was determined using HPV-16 E6 and E7 dPCR assays. N = 4 per condition. Error bars represent SD. Asterisk indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05) in comparison with single-strand capture conditions.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/6535/9401563/8edab22af6e8/5857fig1.gif)

Comment on
-
Selected Articles from This Issue.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 1;27(21):5731. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-27-21-HI. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34725123 No abstract available.
References
-
- Corcoran RB, Chabner BA. Application of cell-free DNA analysis to cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 2018;379:1754–65. - PubMed
-
- Burgener JM, Rostami A, De Carvalho DD, Bratman SV. Cell-Free DNA as a post-treatment surveillance strategy: Current status. Semin Oncol 2017;44:330–46. - PubMed
-
- Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, et al. . Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes. Nature 2018;563:579–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

