Autoimmmune hepatitis
- PMID: 34580437
- PMCID: PMC8475398
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00768-8
Autoimmmune hepatitis
Abstract
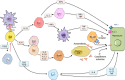
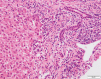
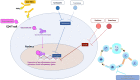
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a T-cell mediated, inflammatory liver disease affecting all ages and characterized by female preponderance, elevated serum transaminase and immunoglobulin G levels, positive circulating autoantibodies, and presence of interface hepatitis at liver histology. AIH type 1, affecting both adults and children, is defined by positive anti-nuclear and/or anti-smooth muscle antibodies, while type 2 AIH, affecting mostly children, is defined by positive anti-liver-kidney microsomal type 1 and/or anti-liver cytosol type 1 antibody. While the autoantigens of type 2 AIH are well defined, being the cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) and the formiminotransferase cyclodeaminase (FTCD), in type 1 AIH they remain to be identified. AIH-1 predisposition is conferred by possession of the MHC class II HLA DRB1*03 at all ages, while DRB1*04 predisposes to late onset disease; AIH-2 is associated with possession of DRB1*07 and DRB1*03. The majority of patients responds well to standard immunosuppressive treatment, based on steroid and azathioprine; second- and third-line drugs should be considered in case of intolerance or insufficient response. This review offers a comprehensive overview of pathophysiological and clinical aspects of AIH.
Keywords: Autoimmune Hepatitis; Genetic Predisposition; Immunopathophysiology; Treatment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. The clinical usage and definition of autoantibodies in immune-mediated liver disease: a comprehensive overview. J Autoimmun. 2018. 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.10.004. - PubMed
-
- Boberg KM, Chapman RW, Hirschfield GM, Lohse AW, Manns MP, Schrumpf E. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group, Overlap syndromes: the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group (IAIHG) position statement on a controversial issue. J Hepatol. 2011;54:374–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

