Epitranscriptomic signatures in stem cell differentiation to the neuronal lineage
- PMID: 34582322
- PMCID: PMC8677044
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1985348
Epitranscriptomic signatures in stem cell differentiation to the neuronal lineage
Abstract
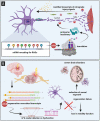
Considered to be a field that is continuously growing, epitranscriptomics analyzes the modifications that occur in RNA transcripts and their downstream effects. As epigenetic modifications found in DNA and histones exhibit specific roles on various biological processes, also epitranscriptomic marks control gene expression patterns that are crucial for proper cell proliferation, differentiation and tissue development. Thus, various epitranscriptomic signatures have been identified to play specific roles during stem cell differentiation towards the neuronal and glial lineages, axonal guidance, synaptic plasticity, thus leading to the development of the mature brain tissue. Here we describe in-depth molecular mechanism underlying the most important RNA modifications with emerging roles in the nervous system.
Keywords: Epitranscriptomic marks; Nm; m6A. m5C; neural development; neural stem cell differentiation; neurodegenerative disease; ψ.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Barbieri I, Kouzarides T. Role of RNA modifications in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(6):303–322. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Sun BF, Xiao W, et al. Dynamic m6A modification and its emerging regulatory role in mRNA splicing. Sci Bull. 2015;60(1):21–32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
