Effects of a low-carbohydrate diet on insulin-resistant dyslipoproteinemia-a randomized controlled feeding trial
- PMID: 34582545
- PMCID: PMC8755039
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab287
Effects of a low-carbohydrate diet on insulin-resistant dyslipoproteinemia-a randomized controlled feeding trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum to Ebbeling et al. Effects of a low-carbohydrate diet on insulin-resistant dyslipoproteinemia-a randomized controlled feeding trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2021;115(1):154-62.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Jan 11;115(1):310. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab372. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35022668 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Carbohydrate restriction shows promise for diabetes, but concerns regarding high saturated fat content of low-carbohydrate diets limit widespread adoption.
Objectives: This preplanned ancillary study aimed to determine how diets varying widely in carbohydrate and saturated fat affect cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors during weight-loss maintenance.
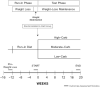
Methods: After 10-14% weight loss on a run-in diet, 164 participants (70% female; BMI = 32.4 ± 4.8 kg/m2) were randomly assigned to 3 weight-loss maintenance diets for 20 wk. The prepared diets contained 20% protein and differed 3-fold in carbohydrate (Carb) and saturated fat as a proportion of energy (Low-Carb: 20% carbohydrate, 21% saturated fat; Moderate-Carb: 40%, 14%; High-Carb: 60%, 7%). Fasting plasma samples were collected prerandomization and at 20 wk. Lipoprotein insulin resistance (LPIR) score was calculated from triglyceride-rich, high-density, and low-density lipoprotein particle (TRL-P, HDL-P, LDL-P) sizes and subfraction concentrations (large/very large TRL-P, large HDL-P, small LDL-P). Other outcomes included lipoprotein(a), triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, adiponectin, and inflammatory markers. Repeated measures ANOVA was used for intention-to-treat analysis.
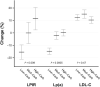
Results: Retention was 90%. Mean change in LPIR (scale 0-100) differed by diet in a dose-dependent fashion: Low-Carb (-5.3; 95% CI: -9.2, -1.5), Moderate-Carb (-0.02; 95% CI: -4.1, 4.1), High-Carb (3.6; 95% CI: -0.6, 7.7), P = 0.009. Low-Carb also favorably affected lipoprotein(a) [-14.7% (95% CI: -19.5, -9.5), -2.1 (95% CI: -8.2, 4.3), and 0.2 (95% CI: -6.0, 6.8), respectively; P = 0.0005], triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, large/very large TRL-P, large HDL-P, and adiponectin. LDL cholesterol, LDL-P, and inflammatory markers did not differ by diet.
Conclusions: A low-carbohydrate diet, high in saturated fat, improved insulin-resistant dyslipoproteinemia and lipoprotein(a), without adverse effect on LDL cholesterol. Carbohydrate restriction might lower CVD risk independently of body weight, a possibility that warrants study in major multicentered trials powered on hard outcomes. The registry is available through ClinicialTrials.gov: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02068885.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease risk factors; dietary trial; low-carbohydrate diet; macronutrients; obesity; saturated fat.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition.
Figures

References
-
- Kris-Etherton PM, Krauss RM. Public health guidelines should recommend reducing saturated fat consumption as much as possible: YES. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(1):13–18. - PubMed
-
- Sacks FM, Lichtenstein AH, Wu JHY, Appel LJ, Creager MA, Kris-Etherton PM, Miller M, Rimm EB, Rudel LL, Robinson JGet al. . Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease: a Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;136(3):e1–e23. - PubMed
-
- Jakobsen MU, Dethlefsen C, Joensen AM, Stegger J, Tjonneland A, Schmidt EB, Overvad K. Intake of carbohydrates compared with intake of saturated fatty acids and risk of myocardial infarction: importance of the glycemic index. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(6):1764–8. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Do high carbohydrate diets prevent the development or attenuate the manifestations (or both) of syndrome X? A viewpoint strongly against. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8(1):23–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

