Myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide screened from Liquidambaris Fructus suppress NLRP3 inflammasome components in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 34583676
- PMCID: PMC8480017
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-021-03410-2
Myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide screened from Liquidambaris Fructus suppress NLRP3 inflammasome components in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Liquidambaris Fructus (LF) is the infructescence of Liquidambar formosana. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, LF has been used to treat joint pain, a common symptom of arthritis and rheumatism; however, a lack of pharmacological evidence has limited its applications in modern clinics. Therefore, this study aims to explore the protective effect of LF on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to identify its active ingredients.
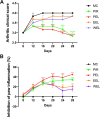
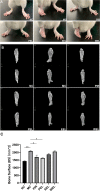
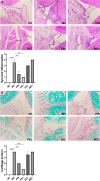
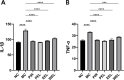
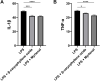
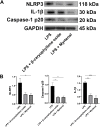
Methods: Rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) were divided into 4 groups and administered petroleum ether extract of LF (PEL), ethyl acetate extract of LF (EEL), water extract of LF (WEL), or piroxicam (PIR) respectively for 3 weeks. Two additional groups were used as normal control (NC) and model control (MC) and administered distilled water as a placebo. The clinical scores for arthritis, bone surface, synovial inflammation and cartilage erosion were used to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of each treatment. The serum IL-1β and TNF-α level and the expression of NLRP3, IL-1β and caspase-1 p20 in the synovial tissue of AIA rats were evaluated by ELISA and Western blot. The active ingredients of LF were investigated using network pharmacology and molecular docking methods, and their inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation was verified in the human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells (RA-FLS) model.
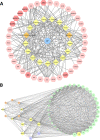
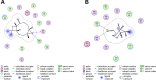
Results: PEL could alleviate paw swelling, bone and joint destruction, synovial inflammation and cartilage erosion in the AIA rats, with significantly superior efficacy to that of EEL and WEL. PEL reduced IL-1β and TNF-α serum levels, and attenuated the upregulation of NLRP3, IL-1β and caspase-1 p20 expression in the synovial tissue of AIA rats. Network pharmacology and molecular docking results indicated that myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide were the main two active ingredients of PEL, and these two compounds showed significant inhibition on TNF-α, NLRP3, IL-1β and caspase-1 p20 expression in RA-FLS.
Conclusions: Myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide screened from PEL could suppress the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby alleviating RA symptoms.
Keywords: Liquidambaris Fructus; Myrtenal; NLRP3 inflammasome; Rheumatoid arthritis; β-Caryophyllene oxide.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TNF-α/calreticulin dual signaling induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation associated with HuR nucleocytoplasmic shuttling in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2019 Jul;68(7):597-611. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01244-w. Epub 2019 May 22. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31119302
-
NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Nov;194(2):231-243. doi: 10.1111/cei.13167. Epub 2018 Sep 16. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30277570 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats and molecular docking studies of Polygonum orientale L. extracts.Immunol Lett. 2018 Sep;201:59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30471320
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Inflammation. 2023 Jun;46(3):835-852. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01795-5. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36897552 Review.
-
A narrative review of positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):12877-12885. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3472. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 35016462 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Drug Repurposing for Anti-Inflammatory Therapy: Virtual Search for Dual Inhibitors of Caspase-1 and TNF-Alpha.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 4;11(12):1832. doi: 10.3390/biom11121832. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944476 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Composite Oral Fast Disintegrating Film: An Innovative Strategy for the Codelivery of Ranitidine HCl and Flurbiprofen.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 20;15(7):1987. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071987. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514173 Free PMC article.
-
Myrtenal Pretreatment Exerts a Protective Effect Against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Mar;39(3):e70202. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70202. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40025781 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Myrtenal and Its Derivatives-A Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;13(10):2086. doi: 10.3390/life13102086. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesquiterpene-evoked phytochemical toxicity in PC12 neuronal cells reveals a variable degree of oxidative stress and alpha-tocopherol and glutathione-dependent protection.Curr Res Toxicol. 2023 Dec 16;6:100144. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2023.100144. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38193034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croia C, Bursi R, Sutera D, Petrelli F, Alunno A, Puxeddu I. One year in review 2019: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37:347–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

