A guide in lentiviral vector production for hard-to-transfect cells, using cardiac-derived c-kit expressing cells as a model system
- PMID: 34584147
- PMCID: PMC8478948
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-98657-7
A guide in lentiviral vector production for hard-to-transfect cells, using cardiac-derived c-kit expressing cells as a model system
Abstract
Gene therapy revolves around modifying genetic makeup by inserting foreign nucleic acids into targeted cells via gene delivery methods to treat a particular disease. While the genes targeted play a key role in gene therapy, the gene delivery system used is also of utmost importance as it determines the success of gene therapy. As primary cells and stem cells are often the target cells for gene therapy in clinical trials, the delivery system would need to be robust, and viral-based entries such as lentiviral vectors work best at transporting the transgene into the cells. However, even within lentiviral vectors, several parameters can affect the functionality of the delivery system. Using cardiac-derived c-kit expressing cells (CCs) as a model system, this study aims to optimize lentiviral production by investigating various experimental factors such as the generation of the lentiviral system, concentration method, and type of selection marker. Our findings showed that the 2nd generation system with pCMV-dR8.2 dvpr as the packaging plasmid produced a 7.3-fold higher yield of lentiviral production compared to psPAX2. Concentrating the virus with ultracentrifuge produced a higher viral titer at greater than 5 × 105 infectious unit values/ml (IFU/ml). And lastly, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of puromycin selection marker was 10 μg/mL and 7 μg/mL for HEK293T and CCs, demonstrating the suitability of antibiotic selection for all cell types. This encouraging data can be extrapolated and applied to other difficult-to-transfect cells, such as different types of stem cells or primary cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



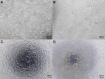

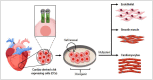

References
-
- Gresch, O. & Altrogge, L. Transfection of difficult-to-transfect primary mammalian cells. in Protein Expression in Mammalian Cells 65–74 (Springer, 2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

