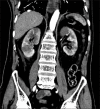
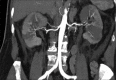
Bilateral Renal Infarcts in a Patient with COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 34584363
- PMCID: PMC8443104
- DOI: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_562_20
Bilateral Renal Infarcts in a Patient with COVID-19 Pneumonia
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
