Diffusion biomarkers in chronic myocardial infarction
- PMID: 34585174
- PMCID: PMC8476206
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-78710-3_14
Diffusion biomarkers in chronic myocardial infarction
Abstract
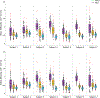
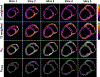
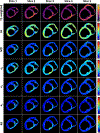
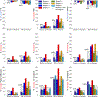
Cardiac diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging (cDTI) allows estimating the aggregate cardiomyocyte architecture in healthy subjects and its remodeling as a result of cardiac disease. In this study, cDTI was used to quantify microstructural changes occurring in swine (N=7) six to ten weeks after myocardial infarction. Each heart was extracted and imaged ex vivo with 1mm isotropic spatial resolution. Microstructural changes were quantified in the border zone and infarct region by comparing diffusion tensor invariants - fractional anisotropy (FA), mode, and mean diffusivity (MD) - radial diffusivity, and diffusion tensor eigenvalues with the corresponding values in the remote myocardium. MD and radial diffusivity increased in the infarct and border regions with respect to the remote myocardium (p<0.01). In contrast, FA and mode decreased in the infarct and border regions (p<0.01). Diffusion tensor eigenvalues also increased in the infarct and border regions, with a larger increase in the secondary and tertiary eigenvalues.
Keywords: Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging; Cardiac Microstructure; Myocardial Infarction; Radial Diffusivity.
Figures

References
-
- Chen J, Song SK, Liu W, McLean M, Allen JS, Tan J, Wickline SA, Yu X: Remodeling of cardiac fiber structure after infarction in rats quantified with diffusion tensor MRI. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 285(3), H946–H954 (2003) - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
