Efficacy of Prucalopride for Chronic Idiopathic Constipation: An Analysis of Participants With Moderate to Very Severe Abdominal Bloating
- PMID: 34585675
- PMCID: PMC8715996
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001521
Efficacy of Prucalopride for Chronic Idiopathic Constipation: An Analysis of Participants With Moderate to Very Severe Abdominal Bloating
Abstract
Introduction: This post hoc analysis evaluated the effect of prucalopride on abdominal bloating in participants with chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) who had moderate to very severe bloating at baseline.
Methods: Data from 6 phase 3/4 studies of prucalopride in participants with CIC were pooled. Abdominal bloating was assessed weekly using a 5-point scale (0-4).
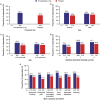
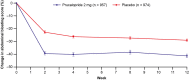
Results: The proportion of bloating responders (≥1-point improvement in abdominal bloating score at week 12) was higher in participants treated with prucalopride (62.1%) vs placebo (49.6%).
Discussion: The prucalopride arm had a higher proportion of bloating responders vs placebo in this study population.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00488137 NCT00483886 NCT00485940 NCT01147926 NCT01116206 NCT01424228.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Camilleri M, Ford AC, Mawe GM, et al. . Chronic constipation. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017;3:17095. - PubMed
-
- Johanson JF, Kralstein J. Chronic constipation: A survey of the patient perspective. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Shire LLC. Motegrity (prucalopride) prescribing information 2020. https://www.shirecontent.com/PI/PDFs/MOTEGRITY_USA_ENG.pdf. Accessed January 18, 2021.
-
- Tack J, Camilleri M, Dubois D, et al. . Association between health-related quality of life and symptoms in patients with chronic constipation: An integrated analysis of three phase 3 trials of prucalopride. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2015;27:397–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

