Increased incidence of COVID-19 in younger patients (May-July 2021)-An argument for extending vaccination?
- PMID: 34585754
- PMCID: PMC8662149
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27363
Increased incidence of COVID-19 in younger patients (May-July 2021)-An argument for extending vaccination?
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
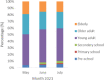
Figures
References
-
- Ladhani SN. Crossing the Rubicon: a fine line between waiting and vaccinating adolescents against COVID‐19. J Infect. 2021;83:294‐297. 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weekly national influenza and COVID‐19 surveillance report week 29 report (up to week 28 data). Public Health England. July 22, 2021. Accessed August 12, 2021. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa...
-
- News—communicating the potential benefits and harms of the Astra‐Zeneca COVID‐19 vaccine. Winton Centre for Risk and Evidence Communication. 2021. Accessed August 15, 2021. https://wintoncentre.maths.cam.ac.uk/news/communicating-potential-benefi...
-
- Sheikh A, McMenamin J, Taylor B, Robertson C, Public Health Scotland and the EAVE II Collaborators . SARS‐CoV‐2 delta VOC in Scotland: demographics, risk of hospital admission, and vaccine effectiveness. Lancet. 2021;397(10293):2461‐2462. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01358-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- SARS‐CoV‐2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England . Technical briefing 20. Public Health England. August 6, 2021. Accessed August 12, 2021. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

