Mini-synplastomes for plastid genetic engineering
- PMID: 34585834
- PMCID: PMC8753362
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13717
Mini-synplastomes for plastid genetic engineering
Abstract
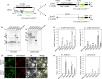
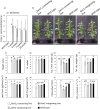
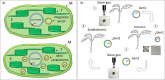
In the age of synthetic biology, plastid engineering requires a nimble platform to introduce novel synthetic circuits in plants. While effective for integrating relatively small constructs into the plastome, plastid engineering via homologous recombination of transgenes is over 30 years old. Here we show the design-build-test of a novel synthetic genome structure that does not disturb the native plastome: the 'mini-synplastome'. The mini-synplastome was inspired by dinoflagellate plastome organization, which is comprised of numerous minicircles residing in the plastid instead of a single organellar genome molecule. The first mini-synplastome in plants was developed in vitro to meet the following criteria: (i) episomal replication in plastids; (ii) facile cloning; (iii) predictable transgene expression in plastids; (iv) non-integration of vector sequences into the endogenous plastome; and (v) autonomous persistence in the plant over generations in the absence of exogenous selection pressure. Mini-synplastomes are anticipated to revolutionize chloroplast biotechnology, enable facile marker-free plastid engineering, and provide an unparalleled platform for one-step metabolic engineering in plants.
Keywords: Solanum tuberosum; episomal replication; homologous recombination; plastid engineering; plastome; small synthetic plastome ‘mini-synplastome’.
© 2021 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Barbrook, A.C. , Dorrell, R.G. , Burrows, J. , Plenderleith, L.J. , Nisbet, R.E. and Howe, C.J. (2012) Polyuridylylation and processing of transcripts from multiple gene minicircles in chloroplasts of the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae . Plant Mol. Biol. 79, 347–357. - PubMed
-
- Barbrook, A.C. and Howe, C.J. (2000) Minicircular plastid DNA in the dinoflagellate Amphidinium operculatum . Mol. Gen. Genet. 263, 152–158. - PubMed
-
- Chiu, W.L. and Sears, B.B. (1992) Electron microscopic localization of replication origins in Oenothera chloroplast DNA. Mol. Gen. Genet. 232, 33–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

