Serological Assays for Assessing Postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response
- PMID: 34585943
- PMCID: PMC8557923
- DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.00733-21
Serological Assays for Assessing Postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response
Abstract
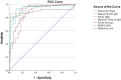
Serological assays for measuring severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antibodies have crucial applications in the control and surveillance of the current COVID-19 pandemic. A large number of such assays have been developed and are now commercially available. However, there are limited studies evaluating the performance of these tests. We evaluated the performances of the following six commercially available serological assays for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: (i) Genscript cPass surrogate virus neutralization test (Genscript cPass), (ii) Diasorin-SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG detection (Diasorin-S1/S2 IgG), (iii) Alinity SARS-CoV-2 IgG II (Alinity IgG II), (iv) Diasorin-SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG (Diasorin-TrimericS IgG), (v) Roche Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2-cobas (Roche Elecsys), and (vi) AESKU enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (AESKULISA). The results of these tests were compared against the gold standard plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT). Roche Elecsys had the highest sensitivity, and the Genscript cPass had the highest specificity. Diasorin-TrimericS IgG had the best overall performance with the highest agreement with the PRNT results. Parallel testing of Genscript cPass with Diasorin-TrimericS IgG and Diasorin-S1/S2 IgG had the optimum performance. Based on the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, lowering the cutoff from 30% to 20% in the Genscript cPass significantly increased the sensitivity and the overall agreement with the PRNT results. Commercially available serological assays are good alternatives to the standard PRNT. However, further studies on larger sample numbers are required for optimization of the assay cutoff values and for evaluation of cost effectiveness. IMPORTANCE Commercial serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are now widely available. This study adds new knowledge regarding the optimization of these assays for evaluating postvaccination antibodies status. It highlights the positive and negative aspects of each assay in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values, compared to the gold standard neutralization test. When using serological assays to assess postvaccine immune status, a balance of all parameters needs to be considered and not simply the high specificity. This balance is particularly relevant in the current situation where countries are aiming to mass vaccinate their populations and bring this pandemic under control. Assays with good sensitivity will have a lower percentage of false negatives and thus provide confidence for vaccination. Understanding the strengths and limitations of commercially available serological assays is important, not only for better application of these tests but also to understand the immune response and the duration of protection postvaccination.
Keywords: CLIA; COVID-19; ELISA; SARS-CoV-2; serological assays.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team . 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghinai I, McPherson TD, Hunter JC, Kirking HL, Christiansen D, Joshi K, Rubin R, Morales-Estrada S, Black SR, Pacilli M, Fricchione MJ, Chugh RK, Walblay KA, Ahmed NS, Stoecker WC, Hasan NF, Burdsall DP, Reese HE, Wallace M, Wang C, Moeller D, Korpics J, Novosad SA, Benowitz I, Jacobs MW, Dasari VS, Patel MT, Kauerauf J, Charles EM, Ezike NO, Chu V, Midgley CM, Rolfes MA, Gerber SI, Lu X, Lindstrom S, Verani JR, Layden JE, Illinois COVID-19 Investigation Team . 2020. First known person-to-person transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the USA. Lancet 395:1137–1144. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30607-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinazzi M, Davis JT, Ajelli M, Gioannini C, Litvinova M, Merler S, Pastore Y Piontti A, Mu K, Rossi L, Sun K, Viboud C, Xiong X, Yu H, Halloran ME, Longini IM, Vespignani A. 2020. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science 368:395–400. doi:10.1126/science.aba9757. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flaxman S, Mishra S, Gandy A, Unwin HJT, Mellan TA, Coupland H, Whittaker C, Zhu H, Berah T, Eaton JW, Monod M, Perez-Guzman PN, Schmit N, Cilloni L, Ainslie KEC, Baguelin M, Boonyasiri A, Boyd O, Cattarino L, Cooper LV, Cucunubá Z, Cuomo-Dannenburg G, Dighe A, Djaafara B, Dorigatti I, van Elsland SL, FitzJohn RG, Gaythorpe KAM, Geidelberg L, Grassly NC, Green WD, Hallett T, Hamlet A, Hinsley W, Jeffrey B, Knock E, Laydon DJ, Nedjati-Gilani G, Nouvellet P, Parag KV, Siveroni I, Thompson HA, Verity R, Volz E, Walters CE, Wang H, Wang Y, Watson OJ, Winskill P, Xi X, Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team, et al. . 2020. Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe. Nature 584:257–261. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2405-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous