Insights in ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 34587242
- PMCID: PMC8483989
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021013231
Insights in ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Abstract
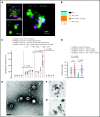
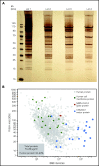
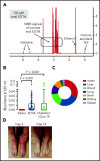
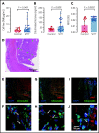
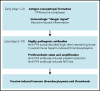
SARS-CoV-2 vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca) causes a thromboembolic complication termed vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT). Using biophysical techniques, mouse models, and analysis of VITT patient samples, we identified determinants of this vaccine-induced adverse reaction. Super-resolution microscopy visualized vaccine components forming antigenic complexes with platelet factor 4 (PF4) on platelet surfaces to which anti-PF4 antibodies obtained from VITT patients bound. PF4/vaccine complex formation was charge-driven and increased by addition of DNA. Proteomics identified substantial amounts of virus production-derived T-REx HEK293 proteins in the ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)-containing vaccine. Injected vaccine increased vascular leakage in mice, leading to systemic dissemination of vaccine components known to stimulate immune responses. Together, PF4/vaccine complex formation and the vaccine-stimulated proinflammatory milieu trigger a pronounced B-cell response that results in the formation of high-avidity anti-PF4 antibodies in VITT patients. The resulting high-titer anti-PF4 antibodies potently activated platelets in the presence of PF4 or DNA and polyphosphate polyanions. Anti-PF4 VITT patient antibodies also stimulated neutrophils to release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in a platelet PF4-dependent manner. Biomarkers of procoagulant NETs were elevated in VITT patient serum, and NETs were visualized in abundance by immunohistochemistry in cerebral vein thrombi obtained from VITT patients. Together, vaccine-induced PF4/adenovirus aggregates and proinflammatory reactions stimulate pathologic anti-PF4 antibody production that drives thrombosis in VITT. The data support a 2-step mechanism underlying VITT that resembles the pathogenesis of (autoimmune) heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


Comment in
-
VITT(al) insights into vaccine-related clots.Blood. 2021 Dec 2;138(22):2159-2160. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014195. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34854882 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vaxzevria (priviously COVID-19 Vaccine Astra Zeneca) : EPAR - Product information, vol. 2021. European Medicines Agency; 2021
-
- Krauel K, Pötschke C, Weber C, et al. . Platelet factor 4 binds to bacteria, [corrected] inducing antibodies cross-reacting with the major antigen in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2011;117(4):1370-1378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

