Founder mutation in myosin-binding protein C with an early onset and a high penetrance in males
- PMID: 34588271
- PMCID: PMC8483030
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2021-001789
Founder mutation in myosin-binding protein C with an early onset and a high penetrance in males
Abstract
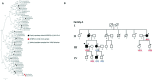
Objective: One of the challenges in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is to determine the pathogenicity of genetic variants and to establish genotype/phenotype correlations. This study aimed to: (1) demonstrate that MYBPC3 c.2149-1G>A is a founder pathogenic variant, (2) describe the phenotype and clinical characteristics of mutation carriers and (3) compare these patients with those with the most frequent pathogenic HCM variants: MYBPC3 p.Arg502Trp/Gln.
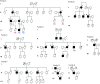
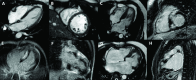
Methods: We reviewed genetic tests performed in HCM probands at our institution. We carried out transcript analyses to demonstrate the splicing effect, and haplotype analyses to support the founder effect of MYBPC3 c.2149-1G>A. Carriers with this mutation were compared with those from MYBPC3 p.Arg502Trp/Gln in terms of presentation features, imaging and outcomes.
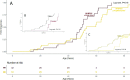
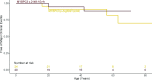
Results: MYBPC3 c.2149-1G>A was identified in 8 of 570 probands and 25 relatives. Penetrance was age and sex dependent, 50.0% of the carriers over age 36 years and 75.0% of the carriers over 40 years showing HCM. Penetrance was significantly higher in males: in carriers older than 30 years old, 100.0% of males vs 50.0% of females had a HCM phenotype (p=0.01). Males were also younger at diagnosis (32±13 vs 53±10 years old, p<0.001). MYBPC3 c.2149-1G>A resulted in an abnormal transcript that led to haploinsufficiency and was segregated in two haplotypes. However, both came from one founder haplotype. Affected carriers showed a better functional class and higher left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) than patients with MYBPC3 p.Arg502Trp/Gln (p<0.05 for both). Nevertheless, the rate of major adverse outcomes was similar between the two groups.
Conclusions: MYBPC3 c.2149-1G>A splicing variant is a founder mutation. Affected males show an early onset of HCM and with higher penetrance than women. Carriers show better functional class and higher LVEF than MYBPC3 p.Arg502Trp/Gln carriers, but a similar rate of major adverse outcomes.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; diagnostic imaging; genetics; hypertrophic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Authors/Task Force members, Elliott PM, Anastasakis A, et al. . 2014 ESC guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the task force for the diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy of the European Society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2014;35:2733–79. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu284 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ommen SR, Mital S, Burke MA, et al. . 2020 AHA/ACC guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 2020;142:e533–57. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000938 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
