Transcription Coactivator BCL3 Acts as a Potential Regulator of Lipid Metabolism Through the Effects on Inflammation
- PMID: 34588797
- PMCID: PMC8476110
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S327858
Transcription Coactivator BCL3 Acts as a Potential Regulator of Lipid Metabolism Through the Effects on Inflammation
Abstract
Background and purpose: Transcriptional coactivator B-cell lymphoma-3 (BCL3) is a member of the IκB family of NF-κB inhibitors and regulates the activity of the NF-κB pathway. However, the relationship between BCL3 and lipid metabolism remains unclear. The present study investigates the effects of BCL3 in immune and metabolism in obese mice.
Animals and methods: Construct Bcl3-KO mice through CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Obesity model was induced in Bcl3-KO mice by feeding a high-fat diet for 16 weeks, and some metabolic-related indicators were analysed.
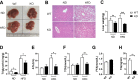
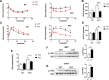
Results: The results showed that the KO mice gained significantly less body weight on a high fat diet without a change in food intake. There was significant improvement in hepatic steatosis and adipose tissue hypertrophy in KO mice. The expression of SREBP1 and its downstream fatty acid synthetase FAS and ACC were down-regulated in KO mice, and the inflammation in adipose tissue and liver was further reduced.
Conclusion: These results suggest that BCL3 may be a novel factor in regulating lipid metabolism in the development of obesity.
Keywords: BCL3; SREBP1; inflammation; lipid metabolism; obesity.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

