Migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh are potential carriers of multi-drug resistant Enterococcus spp., Salmonella spp., and Vibrio spp
- PMID: 34588913
- PMCID: PMC8459117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.053
Migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh are potential carriers of multi-drug resistant Enterococcus spp., Salmonella spp., and Vibrio spp
Abstract
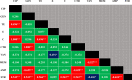
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major health crisis globally. Migratory birds could be a potential source for antibiotic resistant (ABR) bacteria. Not much is known about their role in the transmission of ABR in Bangladesh. In this study, a total of 66 freshly dropped fecal materials of migratory birds were analyzed. Bacterial isolation and identification were based on cultural properties, biochemical tests, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The disk diffusion method was employed to evaluate antibiogram profiles. By PCR, out of 66 samples, the detection rate of Enterococcus spp. (60.61%; 95% confidence interval: 48.55-71.50%) was found significantly higher than Salmonella spp. (21.21%; 95% CI: 13.08-32.51%) and Vibrio spp. (39.40%; 95% CI: 28.50-51.45%). Enterococcus isolates were frequently found resistant (100-40%) to ampicillin, streptomycin, meropenem, erythromycin, and gentamicin; Salmonella isolates were frequently resistant (72-43%) to chloramphenicol, tetracycline, ampicillin, streptomycin, and erythromycin; and Vibrio spp. isolates were frequently resistant (77-31%) to vancomycin, ampicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, and streptomycin. In addition, 60% (95% CI: 44.60-73.65%) Enterococcus spp., 85.71% (95% CI: 60.06-97.46%) Salmonella spp., and 76.92% (95% CI: 57.95-88.97%) Vibrio spp. isolates were multi-drug resistant (MDR) in nature. Three isolates (one from each bacterium) were found resistant against six classes of antibiotics. The bivariate analysis revealed strong associations (both positive and negative) between several antibiotic pairs which were resistant to isolated organisms. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study in detecting MDR Enterococcus spp., Salmonella spp., and Vibrio spp. from migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh. Frequent detection of MDR bacteria from migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh suggests that these birds have the potential to carry and spread ABR bacteria and could implicate potential risks to public health. We recommend that these birds should be kept under an AMR surveillance program to minimize the potential risk of contamination of the environment with ABR as well as to reduce their hazardous impacts on health.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Bacteria; Environment; MDR; Migratory birds; Public health.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Antilles N., García-Bocanegra I., Alba-Casals A., López-Soria S., Pérez-Méndez N., Saco M., González-Solís J., Cerdà-Cuéllar M. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of zoonotic enteropathogens in gulls from southern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;763 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer A.T., Kirby W.M.M., Sherris J.C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966;45:149–158. - PubMed
-
- Brown L.D., Cai T.T., DasGupta A. Interval estimation for a binomial proportion. Stat. Sci. 2001;16:101–117.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

