Advances in Pancreatic Islet Transplantation Sites for the Treatment of Diabetes
- PMID: 34589059
- PMCID: PMC8473744
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.732431
Advances in Pancreatic Islet Transplantation Sites for the Treatment of Diabetes
Abstract
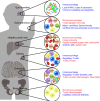
Diabetes is a complex disease that affects over 400 million people worldwide. The life-long insulin injections and continuous blood glucose monitoring required in type 1 diabetes (T1D) represent a tremendous clinical and economic burdens that urges the need for a medical solution. Pancreatic islet transplantation holds great promise in the treatment of T1D; however, the difficulty in regulating post-transplantation immune reactions to avoid both allogenic and autoimmune graft rejection represent a bottleneck in the field of islet transplantation. Cell replacement strategies have been performed in hepatic, intramuscular, omentum, and subcutaneous sites, and have been performed in both animal models and human patients. However more optimal transplantation sites and methods of improving islet graft survival are needed to successfully translate these studies to a clinical relevant therapy. In this review, we summarize the current progress in the field as well as methods and sites of islet transplantation, including stem cell-derived functional human islets. We also discuss the contribution of immune cells, vessel formation, extracellular matrix, and nutritional supply on islet graft survival. Developing new transplantation sites with emerging technologies to improve islet graft survival and simplify immune regulation will greatly benefit the future success of islet cell therapy in the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: biomaterials; diabetes; islet transplantation; stem cells; vascularization.
Copyright © 2021 Cayabyab, Nih and Yoshihara.
Conflict of interest statement
EY is inventor on licensed patents and patent applications related to the HILOs technology described in this manuscript. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances in Cell Replacement Therapies for Diabetes.Diabetes. 2025 Jul 1;74(7):1068-1077. doi: 10.2337/db25-0037. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40272266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Protection of Stem Cell-Derived Islet Cell Therapy for Treating Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 10;12:716625. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.716625. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34447354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of additives, scaffolds and extracellular matrix components for improvement of human pancreatic islet outcomes in vitro: A systematic review.Islets. 2017 Sep 3;9(5):73-86. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2017.1335842. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Islets. 2017. PMID: 28678625 Free PMC article.
-
Islet Transplantation to the Anterior Chamber of the Eye-A Future Treatment Option for Insulin-Deficient Type-2 Diabetics? A Case Report from a Nonhuman Type-2 Diabetic Primate.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720913256. doi: 10.1177/0963689720913256. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32264703 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreas Islet Transplantation for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Clinical Evidence Review.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015 Sep 1;15(16):1-84. eCollection 2015. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015. PMID: 26644812 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cell based-therapy in diabetes mellitus: experimental and clinical perspectives.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Oct 29;15(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03974-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39468609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Diabetes Research: A Novel Islet Isolation Method from Living Donors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5936. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115936. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892122 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium improves hypoxic injury to protect islet graft function.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Aug 28;49(8):1210-1219. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240349. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39788510 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Adapting Physiology in Functional Human Islet Organogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 26;10:854604. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.854604. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35557947 Free PMC article.
-
Bioengineering the Vascularized Endocrine Pancreas: A Fine-Tuned Interplay Between Vascularization, Extracellular-Matrix-Based Scaffold Architecture, and Insulin-Producing Cells.Transpl Int. 2022 Aug 25;35:10555. doi: 10.3389/ti.2022.10555. eCollection 2022. Transpl Int. 2022. PMID: 36090775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

