Rapid Detection and Quantification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA in Paraffinized Samples by Droplet Digital PCR: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 34589075
- PMCID: PMC8475183
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.727774
Rapid Detection and Quantification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA in Paraffinized Samples by Droplet Digital PCR: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
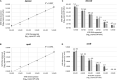
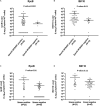
Background: Rapid and reliable diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) represents a diagnostic challenge in compartmentalized extrapulmonary TB infection because of the small number of mycobacteria (MTB) and the frequent lack of fresh samples to perform culture. Here, we estimate the performances of homemade droplet digital PCR (ddPCR)-based assays against culture in 89 biopsies, for those fresh and formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) subsamples were available. Methods: MTB diagnosis in fresh subsamples was performed by culture. Fresh subsamples were also analyzed for acid-fast bacilli smear-microscopy (AFB) and Xpert® MTB/RIF (Xpert). MTB examination was repeated in blind in the 89 FFPE subsamples by in-house ddPCR assays targeting the IS6110 and rpoB. Analytical sensitivity of ddPCR assays was evaluated using serial dilution of H37Rv strain. Limit of detection (LOD) was calculated by probit analysis. Results were expressed in copies/106 cells. Results: IS6110 and rpoB ddPCR assays showed a good linear correlation between expected and observed values (R 2: 0.9907 and 0.9743, respectively). Probit analyses predicted a LOD of 17 and 40 copies/106 cells of MTB DNA for IS6110 and rpoB, respectively. Of the 89 biopsies, 68 were culture positive and 21 were culture negative. Considering mycobacterial culture as reference method, IS6110 assay yielded positive results in 67/68 culture-positive samples with a median interquartile range (IQR) of 1,680 (550-8,444) copies/106 cells (sensitivity: 98.5%; accuracy: 98.9). These performances were superior to those reported by the rpoB assay in FFPE subsamples (sensitivity: 66.20%; accuracy: 74.1) and even superior to those reported by Xpert and AFB in fresh subsamples (sensitivity: 79.4 and 33.8%, respectively; accuracy: 84.3 and 49.4, respectively). When Xpert and AFB results were stratified according to mycobacterial load detected by rpoB and IS6110 ddPCR, bacterial load was lower in Xpert and AFB negative with respect to Xpert and AFB-positive samples (p = 0.003 and 0.01 for rpoB and p = 0.01 and 0.11 for IS6110), confirming the poor sensitivity of these methods in paucibacillary disease. Conclusion: ddPCR provides highly sensitive, accurate, and rapid MTB diagnosis in FFPE samples, as defined by the high concordance between IS6110 assay and culture results. This approach can be safely introduced in clinical routine to accelerate MTB diagnosis mainly when culture results remain unavailable.
Keywords: MTB; MTB diagnosis; ddPCR; extrapulmonary TB; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2021 Antonello, Scutari, Lauricella, Renica, Motta, Torri, Russo, Gentile, Cento, Colagrossi, Mattana, Codecasa, Vismara, Scaglione, Veronese, Bonoldi, Bandera, Gori, Mazzola, Perno and Alteri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alteri C., Cento V., Antonello M., Colagrossi L., Merli M., Ughi N., et al. (2020). Detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 by droplet digital PCR in real-time PCR negative nasopharyngeal swabs from suspected COVID-19 patients. PLoS One 15:236311. 10.1371/journal.pone.0236311 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

