An engineered probiotic secreting Sj16 ameliorates colitis via Ruminococcaceae/butyrate/retinoic acid axis
- PMID: 34589596
- PMCID: PMC8459592
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10219
An engineered probiotic secreting Sj16 ameliorates colitis via Ruminococcaceae/butyrate/retinoic acid axis
Abstract
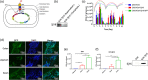
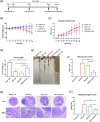
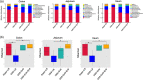
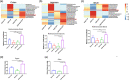
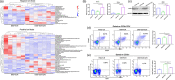
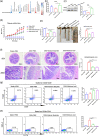
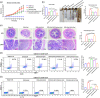
Most inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients are unable to maintain a lifelong remission. Developing a novel therapeutic strategy is urgently needed. In this study, we adopt a new strategy to attenuate colitis using the Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 probiotic strain to express a schistosome immunoregulatory protein (Sj16) in the gastrointestinal tract. The genetically engineered Nissle 1917 (EcN-Sj16) highly expressed Sj16 in the gastrointestinal tracts of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice and significantly attenuated the clinical activity of colitis mice. Mechanistically, EcN-Sj16 increased the intestinal microbiota diversity and selectively promoted the growth of Ruminococcaceae and therefore enhanced the butyrate production. Butyrate induced the expression of retinoic acid, which further attenuated the clinical activity of colitis mice by increasing Treg cells and decreasing Th17. Strikingly, retinoic acid inhibitor inhibited the therapeutic effects of EcN-Sj16 in colitis mice. These findings suggest that EcN-Sj16 represents a novel engineered probiotic that may be used to treat IBD.
Keywords: Ruminococcaceae/butyrate/retinoic acid axis; Sj16; Treg/Th17 balance; colitis; engineered probiotic.
© 2021 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Sun Y, Duan B, Chen H, Xu X. A novel strategy for treating inflammatory bowel disease by targeting delivery of methotrexate through Glucan particles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(6):e1901805. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Shen W, Shi X, et al. Alpha‐tocopheryl succinate‐conjugated G5 PAMAM dendrimer enables effective inhibition of ulcerative colitis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(14):1700276. - PubMed
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population‐based studies. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769‐2778. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

