Hepatitis B Vaccines
- PMID: 34590138
- PMCID: PMC8482019
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa668
Hepatitis B Vaccines
Abstract
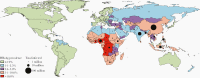
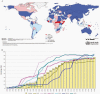
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which infects the liver and may lead to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. HBV represents a worldwide public health problem, causing major morbidity and mortality. Affordable, safe, and effective, hepatitis B vaccines are the best tools we have to control and prevent hepatitis B. In 2019, coverage of 3 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine reached 85% worldwide compared to around 30% in 2000. The effective implementation of hepatitis B vaccination programs has resulted in a substantial decrease in the HBV carrier rate and hepatitis B-related morbidity and mortality. This article summarizes the great triumphs of the hepatitis B vaccine, the first anticancer and virus-like-particle-based vaccine. In addition, existing unresolved issues and future perspectives on hepatitis B vaccination required for global prevention of HBV infection are discussed.
Keywords: hepatitis B; hepatitis B vaccination; hepatitis B virus.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
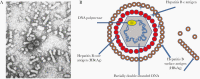
References
-
- Van Damme P, Ward JW, Shouval D, Zanetti A. Hepatitis B Vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein W, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin’s vaccines. 7th Edn. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2017.
-
- Trépo C, Chan HL, Lok A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2014; 384:2053–63. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle JH. Chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 1990; 323:337–9. - PubMed
-
- Edmunds WJ, Medley GF, Nokes DJ, Hall AJ, Whittle HC. The influence of age on the development of the hepatitis B carrier state. Proc Biol Sci 1993; 253:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg BS, Alter HJ, Visnich S. A “new” antigen in leukemia sera. JAMA 1965; 191:541–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

