Environmental risks and toxicity of surfactants: overview of analysis, assessment, and remediation techniques
- PMID: 34590224
- PMCID: PMC8480275
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-16483-w
Environmental risks and toxicity of surfactants: overview of analysis, assessment, and remediation techniques
Abstract
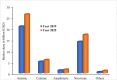
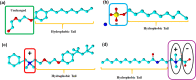
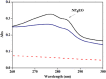
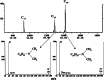
This work comprehensively reviewed the toxicity and risks of various surfactants and their degraded products in the environmental matrices, various analytical procedures, and remediation methods for these surfactants. The findings revealed that the elevated concentration of surfactants and their degraded products disrupt microbial dynamics and their important biogeochemical processes, hinder plant-surviving processes and their ecological niche, and retard the human organic and systemic functionalities. The enormous adverse effects of surfactants on health and the environment necessitate the need to develop, select, and advance the various analytical and assessment techniques to achieve effective identification and quantification of several surfactants in different environmental matrices. Considering the presence of surfactants in trace concentration and environmental matrices, excellent analysis can only be achieved with appropriate extraction, purification, and preconcentration. Despite these pre-treatment procedures, the chromatographic technique is the preferred analytical technique considering its advancement and shortcomings of other techniques. In the literature, the choice or selection of remediation techniques for surfactants depends largely on eco-friendliness, cost-implications, energy requirements, regeneration potential, and generated sludge composition and volume. Hence, the applications of foam fractionation, electrochemical advanced oxidation processes, thermophilic aerobic membranes reactors, and advanced adsorbents are impressive in the clean-up of the surfactants in the environment. This article presents a compendium of knowledge on environmental toxicity and risks, analytical techniques, and remediation methods of surfactants as a guide for policymakers and researchers.
Keywords: Ecotoxicity; Environmental matrix; Ionic surfactants; Non-ionic surfactants; Remediation.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ali TA, Mohamed GG, El-Sonbati AZ, et al. A potentiometric sensor for determination of doxycycline hydrochloride in pharmaceutical preparation and biological fluids. Russ J Electrochem. 2018;54:1081–1095. doi: 10.1134/S1023193518120029. - DOI
-
- Andrew BE. Determination of non-ionic surfactants in waste water by direct extraction with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic detection. Analyst. 1993;118:153–155. doi: 10.1039/AN9931800153. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

