Pathogenicity and virulence of Bordetella pertussis and its adaptation to its strictly human host
- PMID: 34590541
- PMCID: PMC8489951
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1980987
Pathogenicity and virulence of Bordetella pertussis and its adaptation to its strictly human host
Abstract
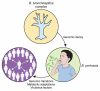
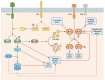
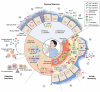
The highly contagious whooping cough agent Bordetella pertussis has evolved as a human-restricted pathogen from a progenitor which also gave rise to Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. While the latter colonizes a broad range of mammals and is able to survive in the environment, B. pertussis has lost its ability to survive outside its host through massive genome decay. Instead, it has become a highly successful human pathogen by the acquisition of tightly regulated virulence factors and evolutionary adaptation of its metabolism to its particular niche. By the deployment of an arsenal of highly sophisticated virulence factors it overcomes many of the innate immune defenses. It also interferes with vaccine-induced adaptive immunity by various mechanisms. Here, we review data from invitro, human and animal models to illustrate the mechanisms of adaptation to the human respiratory tract and provide evidence of ongoing evolutionary adaptation as a highly successful human pathogen.
Keywords: Bordetella; Pertussis; adaptive immunity; evolution; innate immunity; metabolism; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Yeung KHT, Duclos P, Nelson EAS, et al. An update of the global burden of pertussis in children younger than 5 years: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17(9):974–980. - PubMed
-
- Guiso N, Wirsing von Knig CH, Forsyth K, et al. The global pertussis initiative: report from a round table meeting to discuss the epidemiology and detection of pertussis, Paris, France, 11–12 January 2010. Vaccine. 2011;29(6):1115–1121. - PubMed
-
- Hegerle N, Dore G, Guiso N.. Pertactin deficient Bordetella pertussis present a better fitness in mice immunized with an acellular pertussis vaccine. Vaccine. 2014;32(49):6597–6600. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson K, Righolt CH, Elliott LJ, et al. Pertussis vaccine effectiveness and duration of protection - A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine. 2021;39(23):3120–3130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
