First-principles model of optimal translation factors stoichiometry
- PMID: 34590582
- PMCID: PMC8530515
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69222
First-principles model of optimal translation factors stoichiometry
Abstract
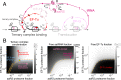
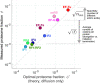
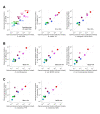
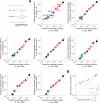
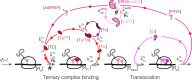
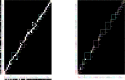
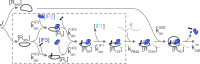
Enzymatic pathways have evolved uniquely preferred protein expression stoichiometry in living cells, but our ability to predict the optimal abundances from basic properties remains underdeveloped. Here, we report a biophysical, first-principles model of growth optimization for core mRNA translation, a multi-enzyme system that involves proteins with a broadly conserved stoichiometry spanning two orders of magnitude. We show that predictions from maximization of ribosome usage in a parsimonious flux model constrained by proteome allocation agree with the conserved ratios of translation factors. The analytical solutions, without free parameters, provide an interpretable framework for the observed hierarchy of expression levels based on simple biophysical properties, such as diffusion constants and protein sizes. Our results provide an intuitive and quantitative understanding for the construction of a central process of life, as well as a path toward rational design of pathway-specific enzyme expression stoichiometry.
Keywords: B. subtilis; E. coli; computational biology; expression stoichiometry; mRNA translation factors; physics of living systems; predictive model; systems biology.
© 2021, Lalanne and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
JL, GL No competing interests declared
Figures

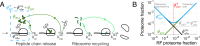


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

