Cone-beam CT angiography to assess the microvascular anatomy of intracranial arterial dissections
- PMID: 34590889
- PMCID: PMC9437491
- DOI: 10.1177/19714009211049089
Cone-beam CT angiography to assess the microvascular anatomy of intracranial arterial dissections
Abstract
Background: Intracranial artery dissection is a rare and generally under-recognized cause of ischaemic stroke or subarachnoid haemorrhage.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to analyse the efficacy of cone-beam computed tomography angiography (CBCT-A) to detect arterial ultrastructural alterations in intracranial artery dissection.
Method: This is an observational and retrospective case series.
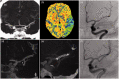
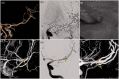
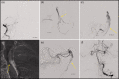
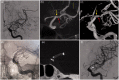
Results: Between January 2018 and November 2020, four patients were admitted with an acute ischaemic stroke due to intracranial dissection studied with CBCT-A. In all cases, the CBCT-A documented vascular ultrastructural alterations related with the intracranial dissection.
Conclusions: CBCT-A is an intraprocedural diagnostic technique that is useful for the diagnosis of intracranial dissections.
Keywords: Cone beam CT; intracranial dissection; intracranial stent; stroke; thrombectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Anson J, Crowell RM. Cervicocranial arterial dissection. Neurosurgery 1991; 29: 89–96. - PubMed
-
- Ohkuma H, Suzuki S, Ogane K; Study Group of the Association of Cerebrovascular Disease in Tohoku, Japan. Dissecting aneurysms of intracranial carotid circulation. Stroke 2002; 33: 941–947. - PubMed
-
- Labeyrie M-A, Civelli V, Reiner P, et al. Prevalence and treatment of spontaneous intracranial artery dissections in patients with acute stroke due to intracranial large vessel occlusion . J Neurointerv Surg 2018; 10: 761–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

