Early IFN-α signatures and persistent dysfunction are distinguishing features of NK cells in severe COVID-19
- PMID: 34592166
- PMCID: PMC8416549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.09.002
Early IFN-α signatures and persistent dysfunction are distinguishing features of NK cells in severe COVID-19
Abstract
Longitudinal analyses of the innate immune system, including the earliest time points, are essential to understand the immunopathogenesis and clinical course of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Here, we performed a detailed characterization of natural killer (NK) cells in 205 patients (403 samples; days 2 to 41 after symptom onset) from four independent cohorts using single-cell transcriptomics and proteomics together with functional studies. We found elevated interferon (IFN)-α plasma levels in early severe COVD-19 alongside increased NK cell expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) and genes involved in IFN-α signaling, while upregulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced genes was observed in moderate diseases. NK cells exert anti-SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) activity but are functionally impaired in severe COVID-19. Further, NK cell dysfunction may be relevant for the development of fibrotic lung disease in severe COVID-19, as NK cells exhibited impaired anti-fibrotic activity. Our study indicates preferential IFN-α and TNF responses in severe and moderate COVID-19, respectively, and associates a prolonged IFN-α-induced NK cell response with poorer disease outcome.
Keywords: COVID-19; NK cells; TNF; antiviral; lung fibrosis; moderate; proteomics; scRNA-seq; severe; type 1 IFN.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.-A.K. and F.I.S. are cofounders and shareholders of Dioscure Therapeutics SE. F.I.S. is a consultant and shareholder of IFM Therapeutics. J.R.H. is founder and board member of Isoplexis and PACT Pharma. J.D.G. declares contracted research with Gilead, Lilly, and Regeneron. K.H., J.M.J., and A.J.B. work at Quanterix Corporation. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
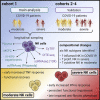



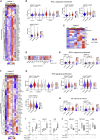
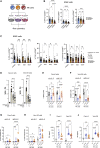
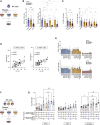
Comment in
-
Profiling natural killers in COVID-19.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Apr;149(4):1223-1224. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 17. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35051507 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Angerer P., Haghverdi L., Büttner M., Theis F.J., Marr C., Buettner F. destiny: diffusion maps for large-scale single-cell data in R. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:1241–1243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

