Subdiffusive-Brownian crossover in membrane proteins: a generalized Langevin equation-based approach
- PMID: 34592261
- PMCID: PMC8595736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.09.033
Subdiffusive-Brownian crossover in membrane proteins: a generalized Langevin equation-based approach
Abstract
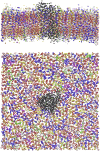
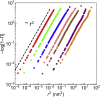
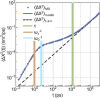
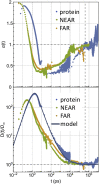
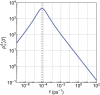
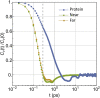
In this work, we propose a generalized Langevin equation-based model to describe the lateral diffusion of a protein in a lipid bilayer. The memory kernel is represented in terms of a viscous (instantaneous) and an elastic (noninstantaneous) component modeled through a Dirac δ function and a three-parameter Mittag-Leffler type function, respectively. By imposing a specific relationship between the parameters of the three-parameter Mittag-Leffler function, the different dynamical regimes-namely ballistic, subdiffusive, and Brownian, as well as the crossover from one regime to another-are retrieved. Within this approach, the transition time from the ballistic to the subdiffusive regime and the spectrum of relaxation times underlying the transition from the subdiffusive to the Brownian regime are given. The reliability of the model is tested by comparing the mean-square displacement derived in the framework of this model and the mean-square displacement of a protein diffusing in a membrane calculated through molecular dynamics simulations.
Copyright © 2021 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subdiffusive behavior in a trapping potential: mean square displacement and velocity autocorrelation function.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2009 Aug;80(2 Pt 1):021111. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.021111. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2009. PMID: 19792081
-
Velocity autocorrelation of a free particle driven by a Mittag-Leffler noise: fractional dynamics and temporal behaviors.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2014 Dec;90(6):062103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.90.062103. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2014. PMID: 25615040
-
Effect of time-dependent temperature and field-bath interaction on the diffusion of generalized Brownian motion.Phys Rev E. 2025 Apr;111(4-1):044126. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.111.044126. Phys Rev E. 2025. PMID: 40411044
-
Non-Brownian diffusion in lipid membranes: Experiments and simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1858(10):2451-2467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.01.022. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26826272 Review.
-
Lipid bilayers, NMR relaxation, and computer simulations.Acc Chem Res. 2002 Jun;35(6):438-46. doi: 10.1021/ar0100529. Acc Chem Res. 2002. PMID: 12069629 Review.
References
-
- Springer T., Lechner R. Volume 1. Springer; New York: 2005. Diffusion in Condensed Matter.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

