Molecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Analysis of Drug-Receptor Interactions in the System Formed by Glargine, Its Metabolite M1, the Insulin Receptor, and the IGF1 Receptor
- PMID: 34594103
- PMCID: PMC8477355
- DOI: 10.1177/11779322211046403
Molecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Analysis of Drug-Receptor Interactions in the System Formed by Glargine, Its Metabolite M1, the Insulin Receptor, and the IGF1 Receptor
Abstract
Introduction: Insulin and insulin-like growth factor type 1 (IGF1) regulate multiple physiological functions by acting on the insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF1R). The insulin analog glargine differs from insulin in three residues (GlyA21, ArgB31, ArgB32), and it is converted to metabolite M1 (lacks residues ArgB31 and ArgB32) by in vivo processing. It is known that activation of these receptors modulates pathways related to metabolism, cell division, and growth. Though, the structures and structural basis of the glargine interaction with these receptors are not known.
Aim: To generate predictive structural models, and to analyze the drug/receptor interactions in the system formed by glargine, its metabolite M1, IR, and IGF1R by using bioinformatics tools.
Methods: Ligand/receptor models were built by homology modeling using SWISSMODEL, and surface interactions were analyzed using Discovery Studio® Visualizer. Target and hetero target sequences and appropriate template structures were used for modeling.
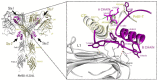
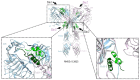
Results: Our glargine/IR and metabolite M1/IR models showed an overall symmetric T-shaped conformation and full occupancy with four ligand molecules. The glargine/IR model revealed that the glargine residues ArgB31 and ArgB32 fit in a hydrophilic region formed by the α-chain C-terminal helix (αCT) and the cysteine-rich region (CR) domain of this receptor, close to the CR residues Arg270-Arg271-Gln272 and αCT residue Arg717. Regarding IGF1R, homologous ligand/receptor models were further built assuming that the receptor is in a symmetrical T-shaped conformation and is fully occupied with four ligand molecules, similar to what we described for IR. Our glargine/IGF1R model showed the interaction of the glargine residues ArgB31 and ArgB32 with Glu264 and Glu305 in the CR domain of IGF1R.
Conclusion: Using bioinformatics tools and predictive modeling, our study provides a better understanding of the glargine/receptor interactions.
Keywords: IGF type 1 receptor; Insulin glargine; insulin receptor; molecular models; protein conformation; receptor protein-tyrosine kinases; theoretical models.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of insulin analogues on insulin/IGF1 hybrid receptors: increased activation by glargine but not by its metabolites M1 and M2.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041992. Epub 2012 Jul 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848683 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro metabolic and mitogenic signaling of insulin glargine and its metabolites.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 4;5(3):e9540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009540. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20209060 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the role of disulfide-linked αCTs in the activation of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and insulin receptor.Elife. 2022 Nov 22;11:e81286. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81286. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36413010 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of disease: metabolic effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1.Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Mar;3(3):302-10. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0427. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17315038 Review.
-
The Role of Nuclear Insulin and IGF1 Receptors in Metabolism and Cancer.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 2;11(4):531. doi: 10.3390/biom11040531. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33918477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

