Trends and Challenges for Population and Health During Population Aging - China, 2015-2050
- PMID: 34594944
- PMCID: PMC8393078
- DOI: 10.46234/ccdcw2021.158
Trends and Challenges for Population and Health During Population Aging - China, 2015-2050
Abstract
What is already known about this topic? As the largest country in the world, China experienced a demographic transition at a historic scale during the past 50 years with extraordinarily associated changes in the age structure of the population, declining fertility rates, accelerating process of population aging, and growing population scale.
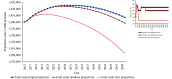
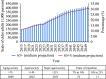
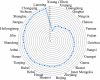
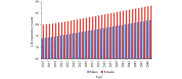
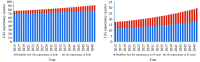
What is added by this report? This study presented future trends of five important population indicators in China. From 2015-2050, China experienced outstanding demographic changes - increases in life expectancy and declines in fertility rate - that have led to population aging. In addition, disability prevalence is growing, and life expectancy with disability is also increasing.
What are the implications for public health practice? This study provided evidence of healthy life expectancy improvement and disease burden declining, healthy aging, and active aging. Due to the uncertainties of future trends of population structure changes, dynamic evaluations, timely adjustments, and innovations in population health strategy design and management should be strengthened to ensure quality of life under the background of population aging.
Keywords: Aging; Challenges; Health; Population; Trends.
Copyright and License information: Editorial Office of CCDCW, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No competing interests declared.
Figures

References
-
- Li CF, Liu HY, Liang Y, Wang H, Li QH Study on international comparison of healthy life expectancy and prediction of healthy life expectancy in China. Populat J. 2018;40(1):5–17. doi: 10.16405/j.cnki.1004-129X.2018.01.001. - DOI
-
-
You YZ, Zheng XY. Mortality and health in the Chinese population levels, patterns, causes and trends since the 1980s. Beijing: Peking University Press. 2005. http://book.kongfz.com/173400/1595914083/.
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
