NP-40 Fractionation and Nucleic Acid Extraction in Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 34595266
- PMCID: PMC8438428
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2584
NP-40 Fractionation and Nucleic Acid Extraction in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
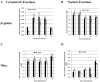
This technique allows for efficient, highly purified cytoplasmic and nuclear-associated compartment fractionation utilizing NP-40 detergent in mammalian cells. The nuclear membrane is not disturbed during the fractionation thus leaving all nuclear and perinuclear associated components in the nuclear fraction. This protocol has been modified from Sambrook and Russell (2001) in order to downscale the amount of cells needed. To determine the efficiency of fractionation, we recommend using qPCR to compare the subcellular compartments that have been purified with equivalent amount of control whole cell extracts.
Keywords: Cell fractionation; Cytoplasmic and nuclear extractions; Nucleic acid purification; Quantitative PCR.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Galvis A. E.(2014). An RNA lariat intermediate in HIV-1 cDNA synthesis. ProQuest 3615193.
-
- Sambrook J. and Russell D. W.(2001). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. CSHL Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

