Machine Learning Applications in the Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Hematological Diseases
- PMID: 34595462
- PMCID: PMC8432325
- DOI: 10.2991/chi.k.201130.001
Machine Learning Applications in the Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Hematological Diseases
Abstract
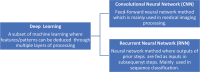
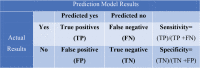
The use of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) methods in hematology includes diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications. This increase is due to the improved access to ML and DL tools and the expansion of medical data. The utilization of ML remains limited in clinical practice, with some disciplines further along in their adoption, such as radiology and histopathology. In this review, we discuss the current uses of ML in diagnosis in the field of hematology, including image-recognition, laboratory, and genomics-based diagnosis. Additionally, we provide an introduction to the fields of ML and DL, highlighting current trends, limitations, and possible areas of improvement.
Keywords: Hematology; artificial intelligence; machine learning.
© 2020 International Academy for Clinical Hematology. Publishing services by Atlantis Press International B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Hematology: Current Challenges and Opportunities.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Jun;15(3):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s11899-020-00575-4. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020. PMID: 32239350 Review.
-
Engineering and clinical use of artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning and data science advancements: radiology leading the way for future.Ther Adv Urol. 2021 Sep 20;13:17562872211044880. doi: 10.1177/17562872211044880. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2021. PMID: 34567272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning in Hematology: From Molecules to Patients.Clin Hematol Int. 2024 Oct 8;6(4):19-42. doi: 10.46989/001c.124131. eCollection 2024. Clin Hematol Int. 2024. PMID: 39417017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Big Data and Machine Learning in Diagnostic Decision Support in Radiology.J Am Coll Radiol. 2018 Mar;15(3 Pt B):569-576. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2018.01.028. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29502585
-
Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology.Br J Haematol. 2021 Jan;192(2):239-250. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16915. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 32602593 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Diagnostic Cytology and Genomic Testing for Hematologic Disorders.Cells. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):1755. doi: 10.3390/cells12131755. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing hematological disorder diagnosis: unraveling the role of artificial intelligence.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Apr 2;87(6):3445-3457. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003227. eCollection 2025 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40486570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Hematology Management: Current Practices and Future Prospects.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Jul 12;24(7):e36490. doi: 10.2196/36490. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35819826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Pattern of Relapse in Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Undergoing Stem Cell Transplant Using Machine Learning Methods.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 10;13(14):4021. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144021. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064061 Free PMC article.
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 and 2 mutations predict better outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a study of the ALWP of the EBMT.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024 Nov;59(11):1534-1541. doi: 10.1038/s41409-024-02384-2. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024. PMID: 39143183
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources