Changes in sleep pattern and dream activity across and after the COVID-19 lockdown in Italy: A longitudinal observational study
- PMID: 34595786
- PMCID: PMC8646575
- DOI: 10.1111/jsr.13500
Changes in sleep pattern and dream activity across and after the COVID-19 lockdown in Italy: A longitudinal observational study
Abstract
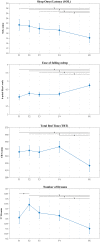
A large body of evidence has documented the impact of the global COVID-19 outbreak - and especially the lockdown period - on sleep quality and quantity. Here, we present the first Italian longitudinal study on sleep and COVID-19 considering four different time points collected during lockdown (from 29 March 2020 to 3 May 2020) and a subsequent follow-up period (October 2020). We used an online survey to collect socio-demographic and COVID-19 related information. Subjects were also asked to complete a sleep diary at each time point of the study. Our longitudinal sample included 147 participants. Statistical comparison across time intervals showed remarkable changes in sleep patterns during and after the lockdown. In particular, during lockdown we observed longer sleep latency, less ease of falling asleep, a higher total bedtime, and a lower dream frequency. The week-by-week evaluation described relatively stable patterns in the observed measures during the lockdown period, except for dream frequency, affected by a rapid increase in the early phase of lockdown. Our findings are in line with the current literature. Furthermore, the prospective longitudinal investigation comprising several time points offered the possibility of (a) observing the temporal dynamics and the different entities of such changes over time, and (b) reducing the typical memory bias for these studies.
Keywords: COVID-19 lockdown; dreaming; longitudinal study; sleep diary; sleep pattern.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Sleep Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Sleep Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have potential conflicts of interest to be disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of the end of COVID confinement on pandemic dreams, as assessed by a weekly sleep diary: a longitudinal investigation in Italy.J Sleep Res. 2022 Feb;31(1):e13429. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13429. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Sleep Res. 2022. PMID: 34288197 Free PMC article.
-
The Oneiric Activity during and after the COVID-19 Total Lockdown in Italy: A Longitudinal Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 24;19(7):3857. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073857. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35409540 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in dream features across the first and second waves of the Covid-19 pandemic.J Sleep Res. 2022 Feb;31(1):e13425. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13425. Epub 2021 Jun 22. J Sleep Res. 2022. PMID: 34159658 Free PMC article.
-
Pandemic dreams: quantitative and qualitative features of the oneiric activity during the lockdown due to COVID-19 in Italy.Sleep Med. 2021 May;81:20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Sleep Med. 2021. PMID: 33631710 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Frequency and Patterns of Marital Sexual Activity During COVID-19: Evidence From Longitudinal Data Prior to, During and After Lockdown in Singapore.J Sex Med. 2022 Feb;19(2):188-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 13. J Sex Med. 2022. PMID: 35058151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic susceptibility and biofilm forming ability of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Jordanian patients with diabetic foot ulcer.Iran J Microbiol. 2024 Aug;16(4):450-458. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v16i4.16303. Iran J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39267929 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Findings on the Oneiric Activity Changes Across the Pandemic.Nat Sci Sleep. 2023 Jun 8;15:435-447. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S410732. eCollection 2023. Nat Sci Sleep. 2023. PMID: 37313311 Free PMC article.
-
Dreaming during the COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jul;138:104710. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104710. Epub 2022 May 25. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35643121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decision-Making and Risk-Propensity Changes during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown.Brain Sci. 2023 May 12;13(5):793. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050793. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239265 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic is associated with increased sleep disturbances and mental health symptoms but not help-seeking: a cross-sectional nation-wide study.Sleep Sci. 2022 Jan-Mar;15(1):1-7. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20220027. Sleep Sci. 2022. PMID: 35662970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimoradi, Z. , Broström, A. , Tsang, H. W. H. , Griffiths, M. D. , Haghayegh, S. , Ohayon, M. M. , … Pakpour, A. H. (2021). Sleep problems during COVID‐19 pandemic and its’ association to psychological distress: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. EClinicalMedicine, 36, 100916. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100916 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altena, E. , Baglioni, C. , Espie, C. A. , Ellis, J. , Gavriloff, D. , Holzinger, B. , … Riemann, D. (2020). Dealing with sleep problems during home confinement due to the COVID‐19 outbreak: Practical recommendations from a task force of the European CBT‐I Academy. Journal of Sleep Research, 29, e13052. 10.1111/jsr.13052 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beck, F. , Leger, D. , Cortaredona, S. , Verger, P. , Peretti‐Watel, P. , Peretti‐Watel, P. , … Léger, D. (2021). Would we recover better sleep at the end of Covid‐19? A relative improvement observed at the population level with the end of the lockdown in France. Sleep Medicine, 78, 115–119. 10.1016/j.sleep.2020.11.029 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical