Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism
- PMID: 34597388
- PMCID: PMC9097250
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab644
Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism
Abstract
Aims: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ACVD) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide, and increased low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) play a critical role in development and progression of atherosclerosis. Here, we examined for the first time gut immunomodulatory effects of the microbiota-derived metabolite propionic acid (PA) on intestinal cholesterol metabolism.
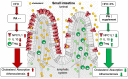
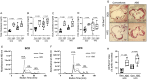
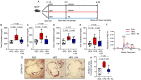
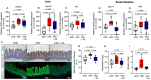
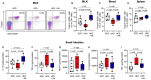
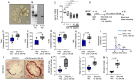
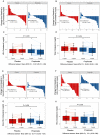
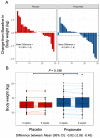
Methods and results: Using both human and animal model studies, we demonstrate that treatment with PA reduces blood total and LDL cholesterol levels. In apolipoprotein E-/- (Apoe-/-) mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD), PA reduced intestinal cholesterol absorption and aortic atherosclerotic lesion area. Further, PA increased regulatory T-cell numbers and interleukin (IL)-10 levels in the intestinal microenvironment, which in turn suppressed the expression of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (Npc1l1), a major intestinal cholesterol transporter. Blockade of IL-10 receptor signalling attenuated the PA-related reduction in total and LDL cholesterol and augmented atherosclerotic lesion severity in the HFD-fed Apoe-/- mice. To translate these preclinical findings to humans, we conducted a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled human study (clinical trial no. NCT03590496). Oral supplementation with 500 mg of PA twice daily over the course of 8 weeks significantly reduced LDL [-15.9 mg/dL (-8.1%) vs. -1.6 mg/dL (-0.5%), P = 0.016], total [-19.6 mg/dL (-7.3%) vs. -5.3 mg/dL (-1.7%), P = 0.014] and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels [PA vs. placebo: -18.9 mg/dL (-9.1%) vs. -0.6 mg/dL (-0.5%), P = 0.002] in subjects with elevated baseline LDL cholesterol levels.
Conclusion: Our findings reveal a novel immune-mediated pathway linking the gut microbiota-derived metabolite PA with intestinal Npc1l1 expression and cholesterol homeostasis. The results highlight the gut immune system as a potential therapeutic target to control dyslipidaemia that may introduce a new avenue for prevention of ACVDs.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Gut microbiome; Propionic acid.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
The promise of the gut metabolite propionate for a novel and personalized lipid-lowering treatment.Eur Heart J. 2022 Feb 10;43(6):534-537. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab723. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 34686871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P, Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M, Nichols M.. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J 2016;37:3232–3245. - PubMed
-
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, Chapman MJ, De Backer GG, Delgado V, Ference BA, Graham IM, Halliday A, Landmesser U, Mihaylova B, Pedersen TR, Riccardi G, Richter DJ, Sabatine MS, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Wiklund O; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J 2020;41:111–188. - PubMed
-
- Brunner FJ, Waldeyer C, Ojeda F, Salomaa V, Kee F, Sans S, Thorand B, Giampaoli S, Brambilla P, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Moitry M, Iacoviello L, Veronesi G, Grassi G, Mathiesen EB, Söderberg S, Linneberg A, Brenner H, Amouyel P, Ferrières J, Tamosiunas A, Nikitin YP, Drygas W, Melander O, Jöckel KH, Leistner DM, Shaw JE, Panagiotakos DB, Simons LA, Kavousi M, Vasan RS, Dullaart RPF, Wannamethee SG, Risérus U, Shea S, de Lemos JA, Omland T, Kuulasmaa K, Landmesser U, Blankenberg S, Zeller T, Kontto J, Männistö S, Metspalu A, Lackner K, Wild P, Peters A, Meisinger C, Donfrancesco C, Signorini SG, Alver M, Woodward M, Gianfagna F, Costanzo S, Wilsgaard T, Eliasson M, Jørgensen T, Völzke H, Dörr M, Nauck M, Schöttker B, Lorenz T, Makarova N, Twerenbold R, Dallongeville J, Dobson A, Malyutina S, Pajak A, Engström G, Bobak M, Schmidt B, Jääskeläinen T, Niiranen T, Jousilahti P, Giles G, Hodge A, Klotsche J, Magliano DJ, Lyngbakken MN, Hveem K, Pitsavos C, Benjamin EJ, Bakker SJL, Whincup P, Ikram MK, Ingelsson M, Koenig W.. Application of non-HDL cholesterol for population-based cardiovascular risk stratification: results from the Multinational Cardiovascular Risk Consortium. Lancet 2019;394:P2173–P2183. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Roberts AB, Buffa JA, Levison BS, Zhu W, Org E, Gu X, Huang Y, Zamanian-Daryoush M, Culley MK, DiDonato AJ, Fu X, Hazen JE, Krajcik D, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL.. Non-lethal inhibition of gut microbial trimethylamine production for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Cell 2015;163:1585–1595. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

